Fig. 1.
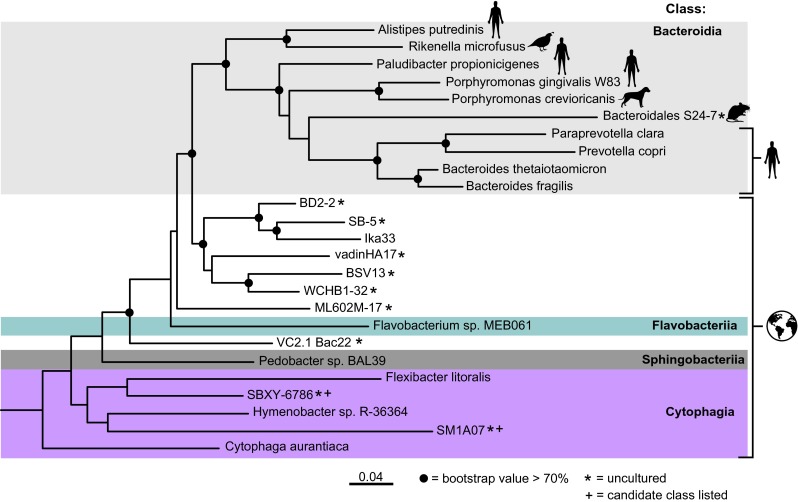
Phylogeny of the Bacteroidetes phylum shows human-associated genera are derived from environmental clades. The 16S rRNA gene sequences used to build this phylogeny were chosen to include representatives of each class within the Bacteroidetes phylum. To add focus on common human-associated Bacteroidetes, additional sequences were included for Alistipes, Prevotella, Bacteroides, S24–7, Rikenella, Porphyromonas, and Paraprevotella. Dictyoglomus thermophilum was used as an outgroup. The tree was built as follows: aligned 16S rRNA sequences (>1300 nt), with high entropy and gapped positions filtered, were used as input for a maximum likelihood phylogenetic estimation in RAxML (assuming a GTR + Υ model of evolution). Nodes on the tree represent >70% bootstrap support (100 replicates). Symbols (human, earth, etc) show the provenance of the sequences. Scale bar units are substitutions/site
