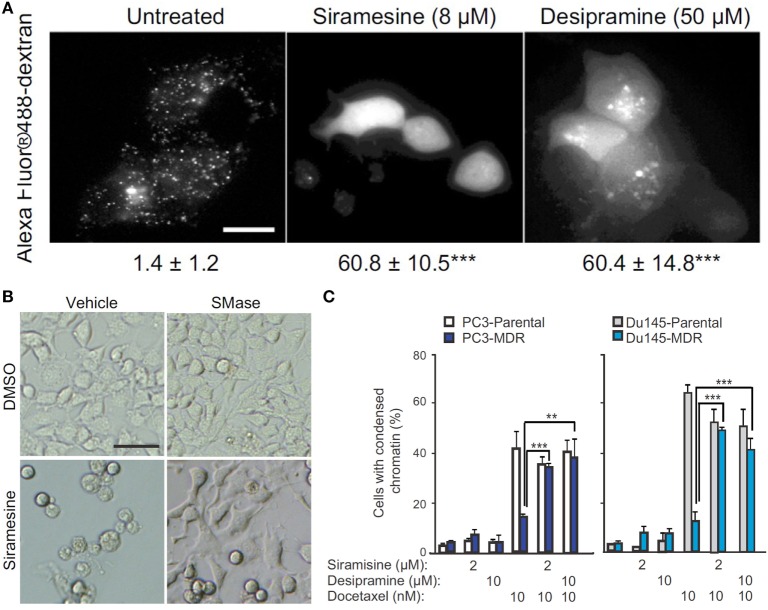
Figure 5.
Targeting acid sphingomyelinases (ASM) is an effective strategy to overcome drug-resistant cancer through lysosome destabilization-mediated cell kill. (A) Siramesine and Desipramine, two cationic amphiphilic drugs and inhibitors of ASM, cause lysosomal membrane permeabilization in MCF-7 cells. The numbers given underneath each image are the respective percentage of cells with lysosomal membrane permeabilization as indicated by cytosolic Alexa Fluor 488-dextran staining. Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) Cell death of transformed NIH 3T3-c-srcY527F cells caused by siramesine can be rescued by adding 75 µM ASM from Bacillus cereus prior to starting drug treatment. Scale bar, 50 µm. (C) ASM inhibition reverts drug resistance of cancer cells. Siramesine and Desipramine treatment of multidrug-resistant (MDR) PC3-MDR or Du145-MDR greatly increased the percentage of cells undergoing apoptotic cell death as evident by condensed chromatin when co-treated with docetaxel. **represents P < 0.01, ***represents P < 0.001. Adapted from Petersen Nikolaj et al. (121).