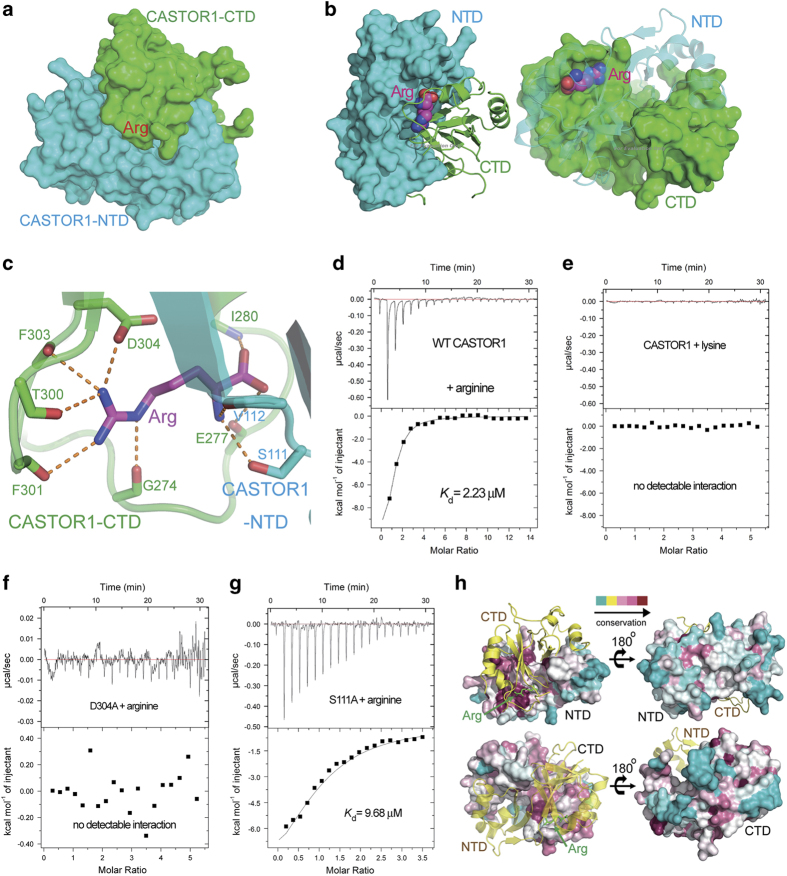
Figure 2.
The arginine-binding pocket of CASTOR1. (a) The arginine is buried between the NTD and the CTD domains of CASTOR1. (b) Both the NTD and the CTD of CASTOR1 employ highly complementary surfaces to recognize the arginine, which is shown in sphere representation. (c) The arginine-binding pocket of CASTOR1. Residues from CASTOR1-NTD or CASTOR1-CTD are colored in cyan or green, respectively. The bound arginine is colored in magenta. Hydrogen bonds are represented as orange dashed lines. (d) The dissociation constant (Kd) between wild-type (WT) CASTOR1 and arginine was measured by ITC to be 2.23 μM. (e) No measurable interaction was detected between CASTOR1 and lysine. (f) Point mutation of Asp304 to alanine disrupted the association between CASTOR1 and arginine. (g) The S111A mutation diminished the binding affinity of CASTOR1 for arginine, with the Kd value increasing to 9.68 μM. (h) The arginine-binding sites on CASTOR1-NTD and -CTD are highly conserved, whereas the outside surface of CASTOR1 is not conserved.