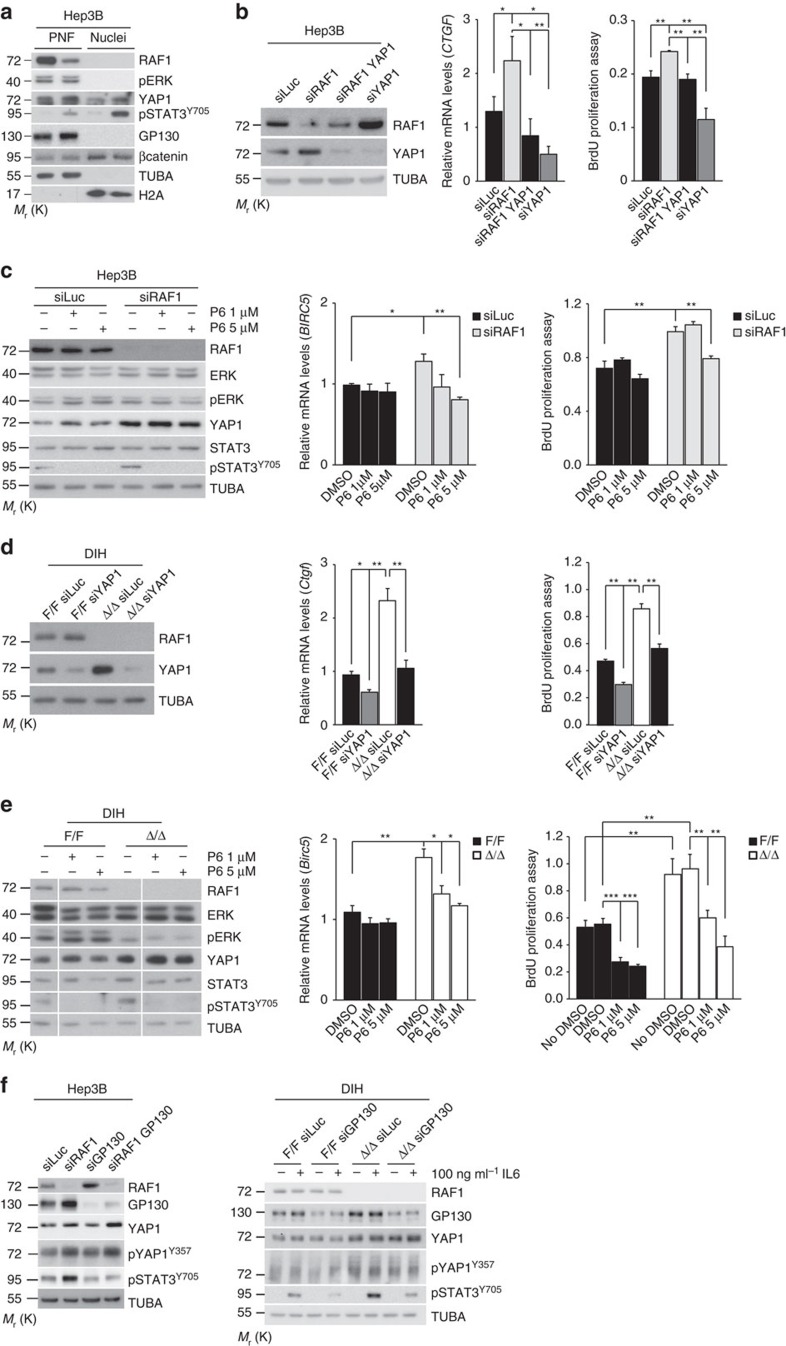
Figure 5. Effect of YAP1 silencing, the P6 JAK inhibitor and GP130 silencing on DIH and Hep3B proliferation.
(a) siRNA-mediated RAF1 silencing in Hep3B cells increases YAP1 and GP130 expression and STAT3 activation without impacting ERK phosphorylation or β-catenin expression/localization. Immunoblot analysis of post-nuclear fraction (PNF; 20 μg, about 8% of total) and nuclear fraction (Nuclei; 20 μg, about 15% of total). (b) Silencing of YAP1 in RAF1-proficient and -deficient Hep3B cells (left panel, representative immunoblot analysis) downregulates the expression of the YAP1 target gene CTGF (middle panel, qPCR analysis) and reduces proliferation (right panel). (c) Treatment with the JAK inhibitor P6 abrogates STAT3 phosphorylation without impacting ERK phosphorylation or YAP1 expression (left panel, representative immunoblot analysis), decreases BIRC5 expression (middle panel, qPCR analysis) and reduces proliferation in RAF1-deficient Hep3B cells (right panel). (d,e) Similar results are obtained by subjecting RAF1-proficient and -deficient DIH to YAP1 silencing (d) or P6 treatment (e). (f) GP130 silencing decreases STAT3 phosphorylation but does not affect YAP1 expression or phosphorylation. Proliferation was assessed 48 h after siRNA transfection (with the exception of c, in which P6 was added 24 h after transfection and proliferation was measured after additional 48 h), gene expression after 24 h, and for immunoblotting cells were lysed after 1 h inhibitor treatment. In (f) DIH were treated for 30 min with the indicated concentration of IL6. Experiments were performed in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS (Hep3B cells) or in DIH medium supplemented with 5% FBS (DIH). The immunoblots are representative of two independent experiments; TUBA was used as loading control. The plots represent the mean±s.e.m. of three independent experiments. *P≤0.05, **P<0.01 according to Student's t test.