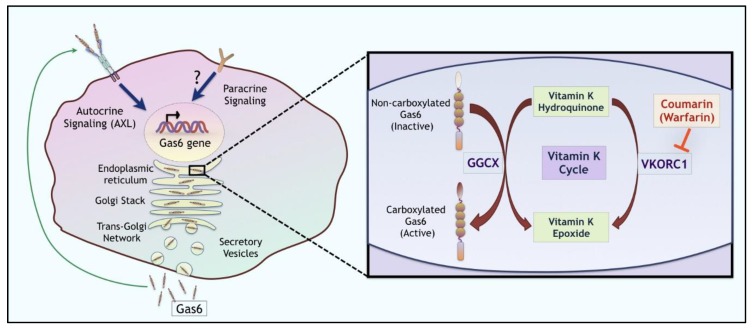
Figure 2.
Post-translational modifications of Gas6 by γ-glutamyl carboxylation. Gas6 can be transcriptionally upregulated by autocrine or paracrine mechanisms. Following translation, un-carboxylated Gas6 (inactive) is activated by a series of enzymatic steps involving γ-glutamyl carboxylation via the vitamin-K-dependent enzyme γ-glutamyl carboxylase (Ggcx). The carboxylated (active) Gas6 from ER is transported to the Golgi apparatus through trans-Golgi network and then into secretory vesicles. The Vit-K epoxide reductase enzyme complex 1 (Vkorc1) then completes the Vit-K cycle by recycling this epoxide back to hydroquinone, which in turn serves as a co-factor in the Ggcx induced γ-carboxylation of Gas6 and Pros1. Warfarin, which functions as a direct inhibitor Vkorc1 prevents γ-carboxylation of Gas6 and Pros1 and prevents TAM receptor activation in the tumor microenvironment.