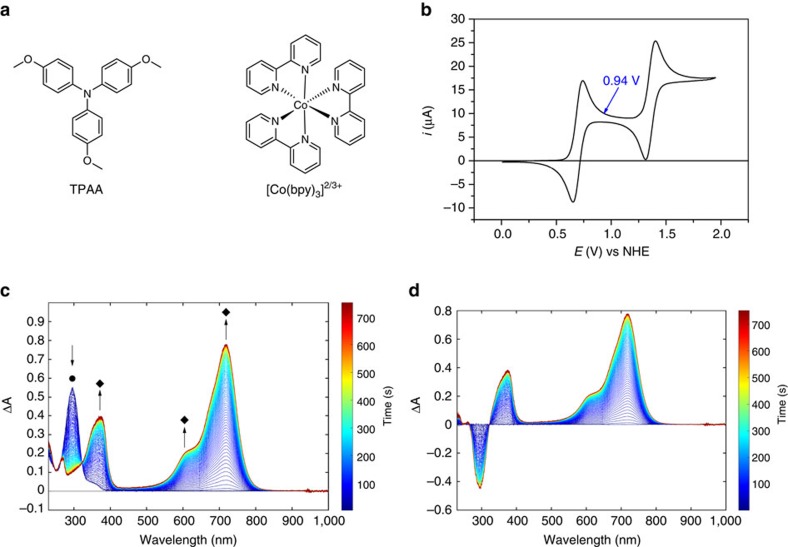
Figure 1. Chemical compounds and electrochemistry.
(a) Chemical structures of TPAA, [Co(bpy)3](PF6)2 and[Co(bpy)3](PF6)3 used in the present study. (b) Cyclic voltammogram of 1 mM TPAA in 0.1 M TBAPF6 in ACN. The arrow indicates the position of applied potential in the spectroelectochemical measurements (vide infra); working electrode: platinum; counter electrode: graphite rod; reference electrode: Ag/AgNO3 (10 mM in ACN). Conversion to the NHE scale was conducted by calibrating the potential of the reference electrode with Fc/Fc+ redox couple (0.635 V versus NHE) after the measurements (c) the evolution of the ultraviolet–visible spectra of TPAA after applying a fixed potential at 0.94 V (versus NHE). Black circle for the absorption peak of TPAA; black diamond marks the absorption peak for TPAA˙+. (d) The graph shows the difference of spectra.