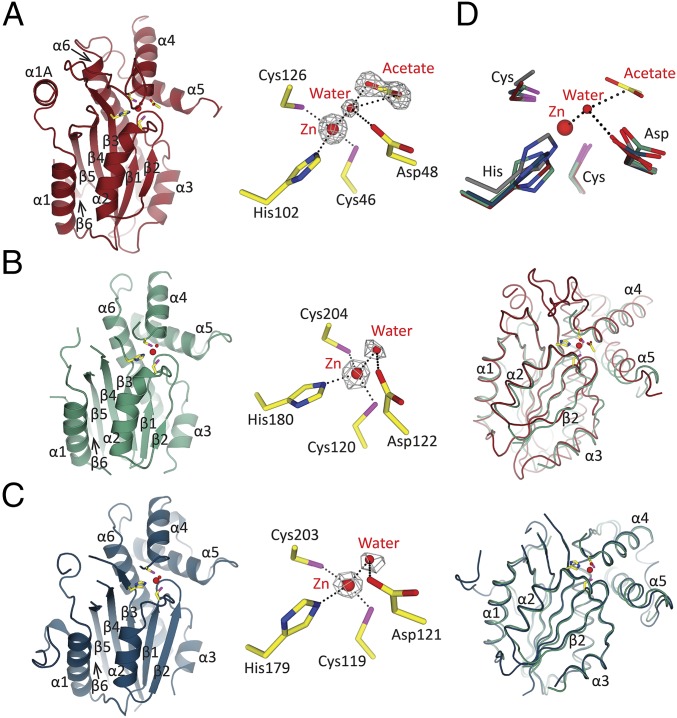
Fig. 2.
Overall structures, active sites, and comparison of CrLCIB-ΔC, CrLCIC-ΔC, and PtLCIB4 subunits. Zn ion and water are colored in bright red and represented as larger and smaller spheres, respectively. The active site residues are in yellow. The Fo-Fc electron density maps are calculated with omission of the enveloped atoms. The side chains of the residues involved in Zn and water binding are shown as sticks, with C, O, and N atoms colored in yellow, red, and blue, respectively (same as below). Coordination of the Zn ion and polar interactions are indicated by dashed lines. (A) The structure of the PtLCIB4 (red, same as below) and the Zn-binding site. The acetate molecule is shown as sticks, with O atom colored in red. (B) The structure of the CrLCIB-ΔC subunit (green, same as below), an enlarged view of the Zn-binding site and the CrLCIB-ΔC subunit overlaid with PtLCIB4. (C) The structure of the CrLCIC-ΔC subunit (blue, same as below), the Zn-binding site, and the CrLCIC-ΔC subunit overlaid with CrLCIB-ΔC. (D) Active site residue superposition of CrLCIB-ΔC (green), CrLCIC-ΔC (blue), PtCIB4 (red), and PSCA (gray). Zn, water, and acetate are from the PtLCIB4 structure. The dashed lines indicate that those atoms are within interacting distance of the water molecule.