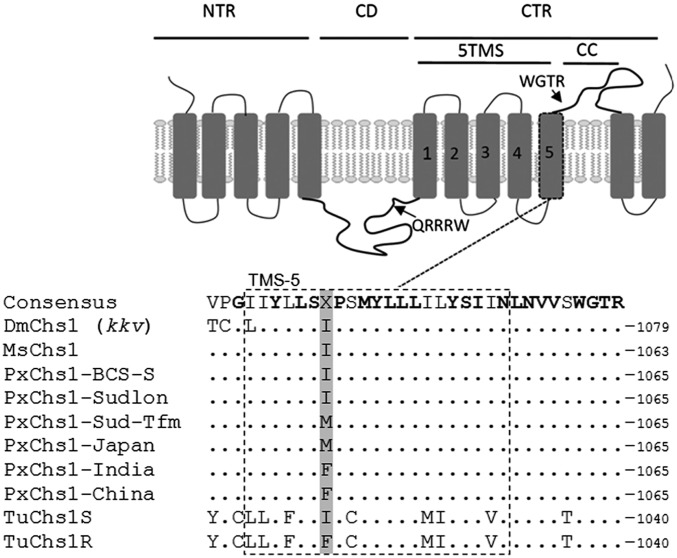
Fig. 2.
Location of the two mutations conferring resistance. (Top) Schematic representation of domain architecture of CHS1, redrafted from ref. 19. 5TMS, cluster of five transmembrane segments; CC, coiled-coil motif; CD, catalytic domain; CTR, C-terminal region; NTR, N-terminal region. Rectangular boxes represent transmembrane domains. Arrows point to signature sequences QRRRW (catalytic domain) and WGTR (N-terminal region). (Bottom) Aligned amino acid sequences of helix 5 in the 5TMS clusters of CHS1 of D. melanogaster (Dm), M. sexta (Ms), six strains of P. xylostella (Px), and T. urticae (Tu; S, etoxazole susceptible; R, etoxazole resistant). Conserved residues are shown in bold. The position of the I1042M/F substitution in resistant P. xylostella (I1017F in etoxazole-resistant mites) is indicated in gray.