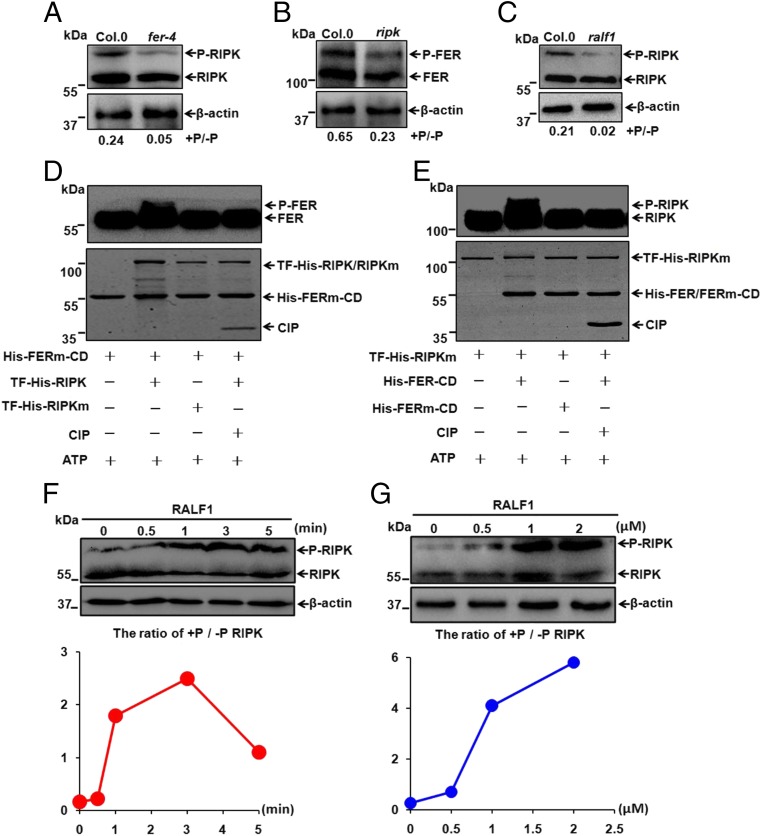
Fig. 3.
Phosphorylations of RIPK and FER are interdependent in response to RALF1 peptide. (A) Phosphorylation status of RIPK in 7-d-old Col.0 and fer-4 Arabidopsis seedlings. The ratio of p-RIPK/RIPK was displayed below the gel, and β-actin was shown as a loading control in A–C, F, and G. (B) Phosphorylation status of FER in 45-d-old Col.0 and ripk-Col.0 plants. (C) Phosphorylation status of RIPK in 7-d-old Col.0 and RALF1-RNAi (ralf1) seedlings. (D and E) In vitro kinase activity assays showing cross-phosphorylation of FER and RIPK kinase domains. These assays were started by adding ATP and analyzed by Western blot using His antibody (1:5,000). Input proteins were visualized by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining (Lower). Data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments with similar results. (F) Time courses (0, 0.5, 1, 3, and 5 min) of RIPK phosphorylation in response to RALF1 peptide (1 μM) using 7-d-old Col.0 Arabidopsis seedlings. (G) RIPK phosphorylation in 7-d-old Col.0 Arabidopsis seedlings after being exposed to different RALF1 concentrations (0, 0.5, 1, and 2 μM) for 3 min.