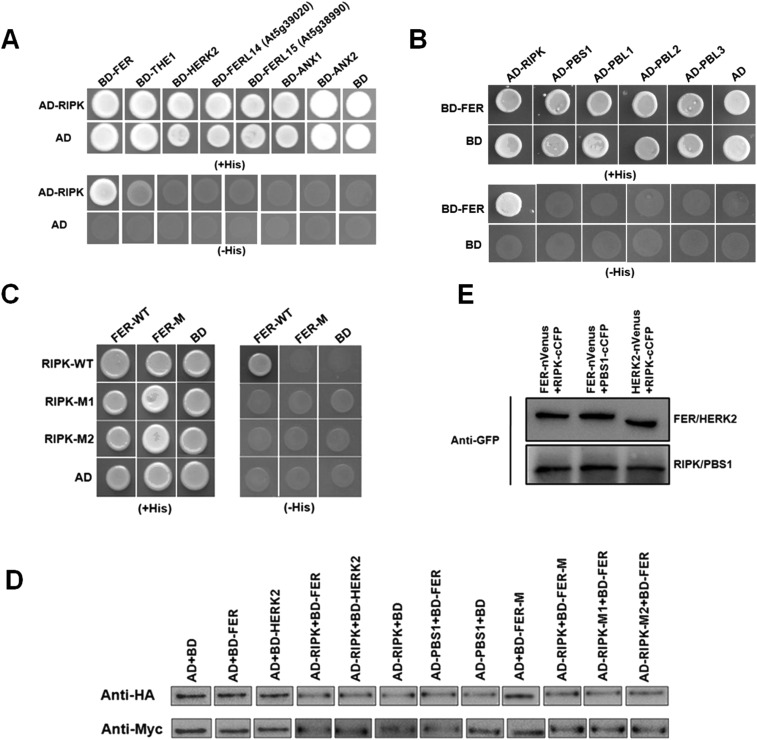
Fig. S3.
RIPK interacts with FER in the Y2H and BiFC system. (A) Y2H analysis of the interaction between RIPK and multiple CrRLK1L subfamily members. RIPK was cloned into the AD vector; FER and other CrRLK1L subfamily members were cloned into the BD vector. Cells were grown on medium with (Upper) or without (Bottom) His. (B) Y2H analysis of interaction between FER and multiple RLCK-VII subfamily members. RIPK and other RLCK-VII subfamily members were cloned into the AD vector; FER was cloned into the BD vector. Cells were grown on medium with (Upper) or without (Bottom) His. (C) RIPK, RIPK-M1 (S251R), and RIPK-M2 (T252R) were cloned into the AD vector; FER and FER-M (K565R) were cloned into the BD vector. Cells were grown on medium with (Left) or without (Right) His. Four independent experiments were conducted, and a representative picture was shown. (D) Protein accumulation of the assay and controls in the BiFC construct as detected by Western blot using GFP antibody (1:5,000). (E) Protein accumulation of the BD baits (fused with the Myc-tag) and AD preys (fused with the HA-tag) in the Y2H system as detected by Western blot.