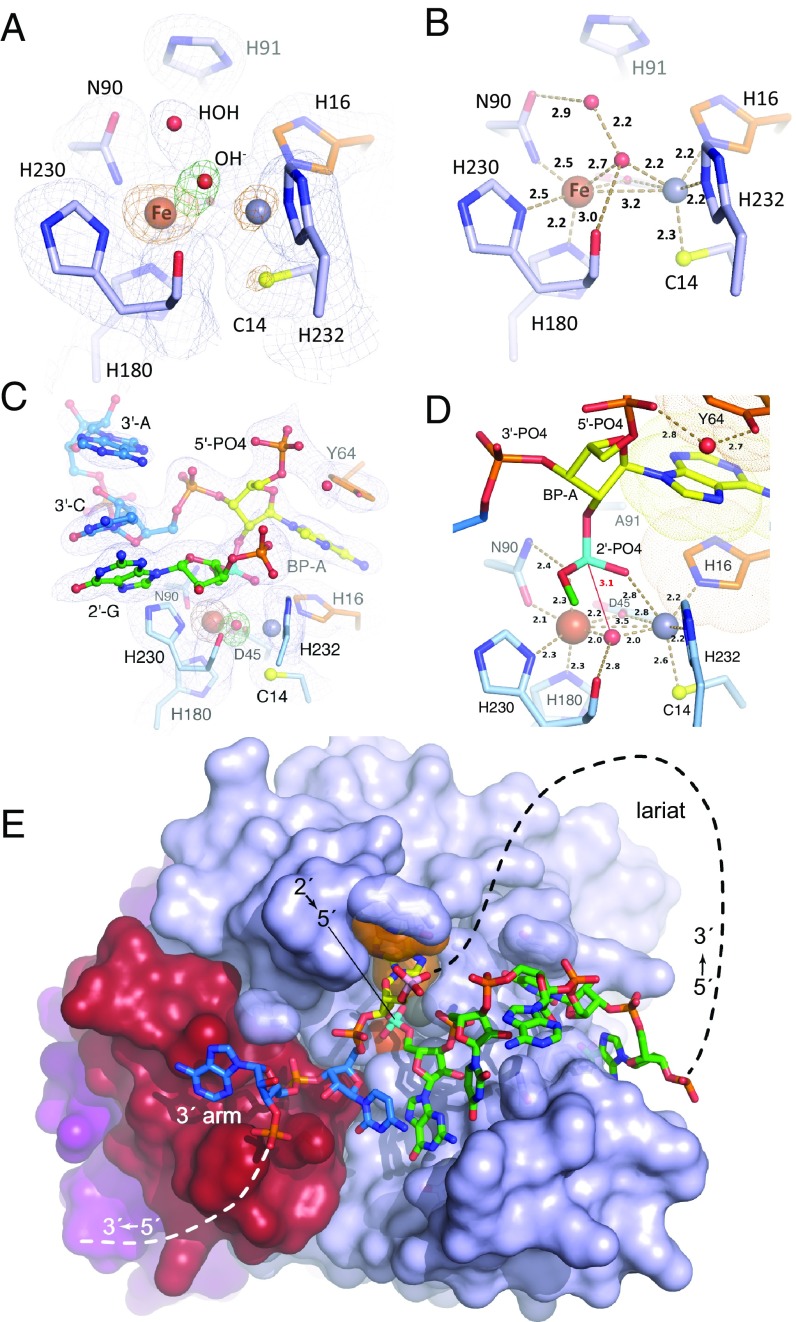
Fig. 3.
Structures of wild-type EhDbr1 alone and its H91A variant in complex with AK49 and AK86. The nucleotide color coding is as in Fig. 1. H16 and Y64 engage in aromatic stacking interactions with the branchpoint adenine and are orange, Fe and Zn ions are rust and gray spheres, respectively, the 2′,5′-linkage is cyan, and the 5′-phosphate of the branchpoint nucleotide is pink. (A) σA-weighted 2Fo-Fc (light blue mesh), Fo-Fc (green mesh), and anomalous difference (orange mesh) electron density maps superimposed on the refined structure of wild-type EhDbr1 contoured at 1.2, 5.0, and 5.0 σ, respectively. The density for the bridging hydroxide is obscured by the metal ion density in the 2Fo-Fc map. The Fo-Fc electron density revealing its position was calculated after removing the hydroxide from the refined model. The anomalous difference map was calculated by using X-rays tuned to the Fe absorption edge (see Results). (B) Coordination distances (Å) for the metal ions in wild-type EhDbr1. The view is the same as in A. (C) σA-weighted 2Fo-Fc, Fo-Fc, and anomalous difference electron density maps superimposed on the refined structure of H91A EhDbr1 in complex with the synthetic 7-mer bRNA AK49 at 1.0, 5.0, and 5.0σ, respectively. (D) Coordination distances for the metal ions shown in C. For clarity, only the 5′-carbon atom of the flanking 2′-G is shown. (E) The 16-mer bRNA AK86 in complex with H91A EhDbr1. The MPE domain is light blue, the lariat recognition loop is red, and the C-terminal domain is purple. The dashed lines indicate the connectivity in the full intron lariat.