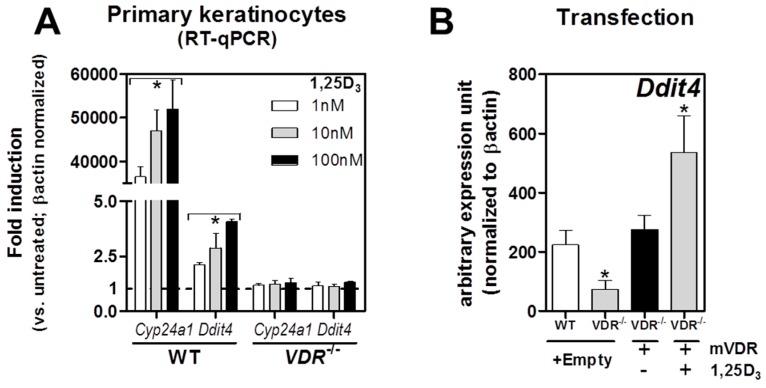
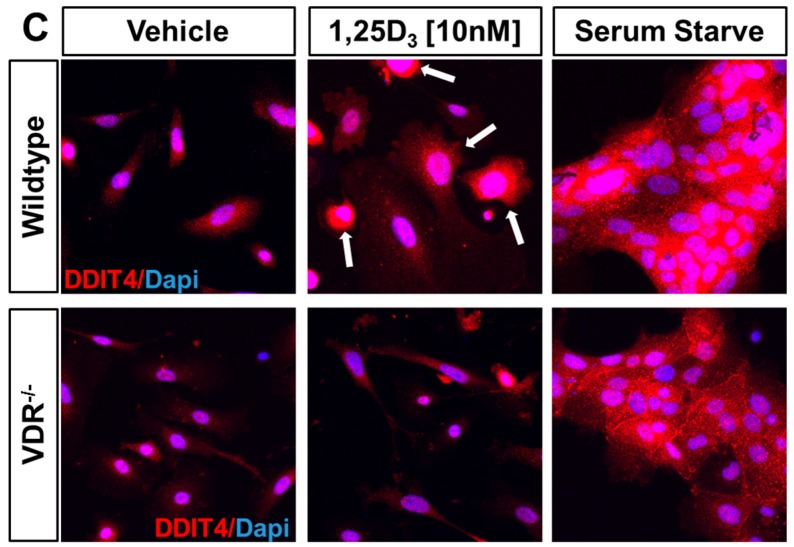
Figure 2.
Regulation of the mechanistic/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor and stress sensor DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 (Ddit4) by liganded vitamin D receptors (VDRs) within primary keratinocytes (column 1.5). (A) Dose-dependent transcriptional induction of Cyp24a1 and Ddit4 by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25D3, 6 h) in wildtype (WT), but not VDR−/−, primary keratinocytes derived from neonatal pups; (B) Transient transfection of VDR−/− primary keratinocytes with a mVDR plasmid restores endogenous Ddit4 transcript levels. Combined treatment further enhanced Ddit4 mRNA levels (with mVDR transfection and 1,25D3 of 10 nM for 6 h); (C) Immunofluorescence detection of Ddit4 within primary keratinocytes. WT, but not VDR−/−, primary keratinocytes exposed to 10 nM 1,25D3 for 18 h resulted in increased intracellular accumulation of Ddit4 (white arrows). Ddit4 upregulation in response to fetal bovine serum deprivation for 24 h in both WT and VDR−/− keratinocytes. One-way ANOVA at an α = 0.05 (95% confidence interval) and Tukey’s multiple comparison post-tests were utilized. Significance is denoted with asterisks: * p < 0.05 (n = 3–4 experiments). RT-qPCR: reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction.