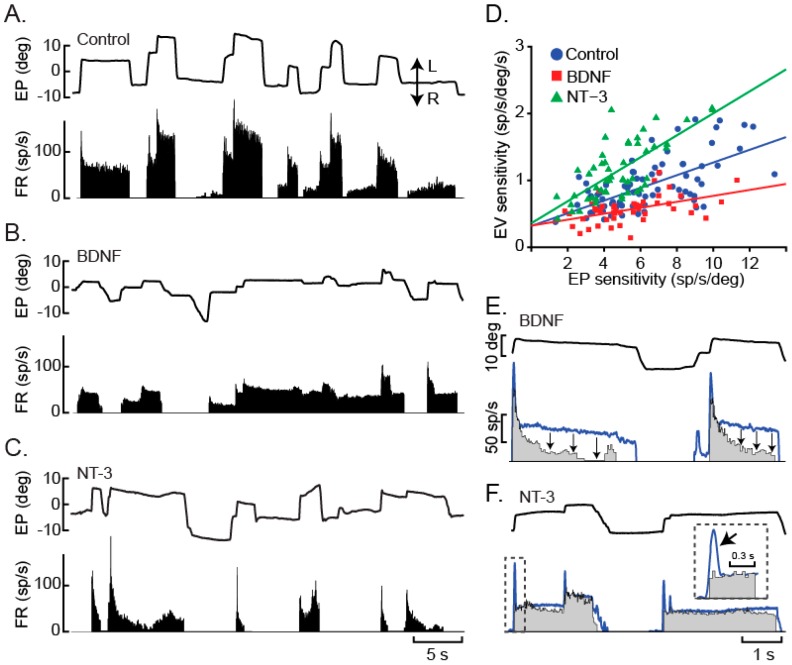
Figure 5.
Complementary firing patterns of BDNF- and NT-3-treated motoneurons: (A) The firing rate (FR, in spikes/s; sp/s) of control motoneurons shows burst for on-directed saccades and a tonic activity during eye fixations; (B) treatment with BDNF for eight days immediately after axotomy reduced bursts in response to saccades; (C) same as (B) but for a seven-day NT-3-treated cell displaying large bursts for saccades but reduced tonic firing for eye fixations; (D) relationship between neuronal eye position (EP, in degrees; deg) and eye velocity (EV) sensitivities obtained by linear regression analysis for 75 control (blue), 45 BDNF-treated (red) and 51 NT-3-treated (green) motoneurons showing that BDNF recovered the tonic (EP), whereas NT-3 restores the phasic (EV) component of discharge activity; and (E) response of a motoneuron (grey firing rate) NT-3-treated for 14 days immediately after axotomy. The blue line represents the firing rate simulation expected for the actual eye movement. Arrows point to the decay in firing rate during fixations; (F) Response of a BDNF-treated motoneuron (grey) for 24 days demonstrating a tonic mode of firing. The blue line as in (E) represents the simulated firing expected for the actual eye movements. The arrow points to the reduced bursts during saccades that are characteristic of BDNF-treated cells that, however, exhibit normal tonic firing. Taken from [105].