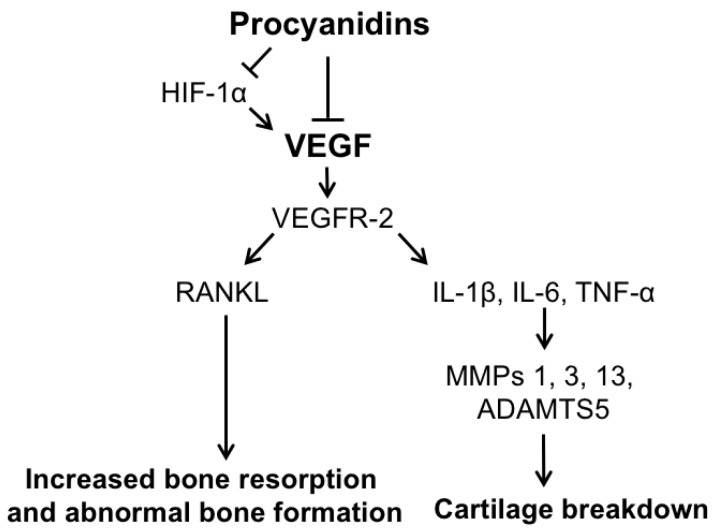
Figure 7.
Hypothesized mechanism of procyanidin-mediated mitigation of OA pathogenesis. Procyanidins suppress expression of VEGF-mediated signaling by suppressing expression of VEGF and phosphorylation of VEGFR-2, and/or indirectly by reducing expression of HIF-1α. Suppression of VEGF-mediated signaling downregulates expression of VEGF and its signaling pathway associated mediators, including pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, and proteolytic enzymes MMP-1, -3, -13, and ADAMTS5, which cleave components of the cartilage extracellular matrix. Procyanidins also suppress VEGF-induced RANKL, preventing increased bone resorption and abnormal bone formation.