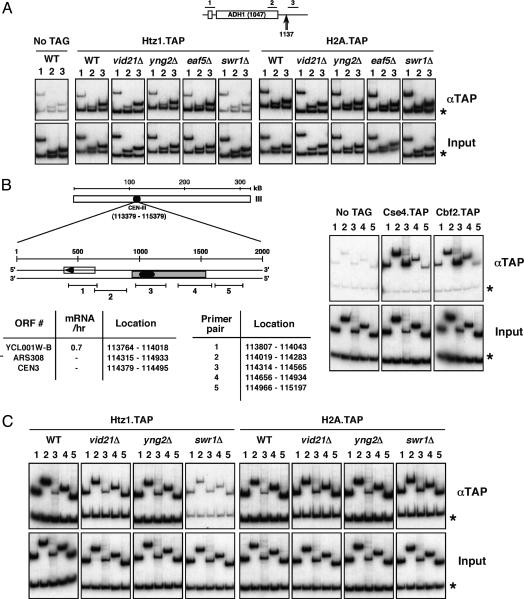
Fig. 4.
Htz1 recruitment is Swr1-dependent and NuA4-independent at all tested regions. (A) ChIP analysis at the ADH1 gene. A schematic of the ADH1 locus is shown with the location of the ChIP primer pairs 1–3 (Upper) and the major polyadenylation/cleavage site at +1137 (Lower) (57). The asterisks indicate a subtelomeric region of chromosome V (9716–9823) that we frequently use as a nontranscribed control when analyzing transcriptionally active regions (5). Chromatin samples from each strain were analyzed after the indicated precipitation. The bottom row is input, used to normalize the PCR amplification efficiency of each primer pair. Equivalent crosslinking of Rpb3 in each case was used as a control for sample integrity (not shown). Whereas swr1Δ leads to a loss of Htz1 occupancy at all tested regions, deletion of members of the NuA4 complex (vid21Δ, yng2Δ, and eaf5Δ) has no detectable effect. (B) A schematic of the chromosome III centromere (CEN-III), with the location of coding sequences, structural elements and ChIP primer pairs depicted. Asterisk indicates a subtelomeric region of chromosome 5 as above. Transcriptional frequency of Ycl001w-b (mRNA/hr) is from ref. 58 (http://web.wi.mit.edu/young/expression/halflife.html). The histone H3 variant Cse4 and the kinetochore component Cbf2 crosslink at the centromere, as reported (59–61). (C) ChIP analysis at CEN-III. Chromatin samples from the indicated strains were analyzed after precipitation via the TAP tag. Htz1 and H2A occupancy at CEN-III (and CEN-V, not shown) is equivalent to that at the subtelomeric (asterisk) region. Htz1 recruitment at this region depends on the SWR-C (indicated by swr1Δ), but independent of NuA4 (indicated by vid21Δ and yng2Δ). H2A recruitment is independent of both complexes. The reduced occupancy at primer pair 3 directly over CEN-III is not unique to Htz1 and is also exhibited by H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 (latter three not shown). This may be a combined function of relative primer efficiency, reduced nucleosome density at this region, and steric occlusion by the kinetochore complex.