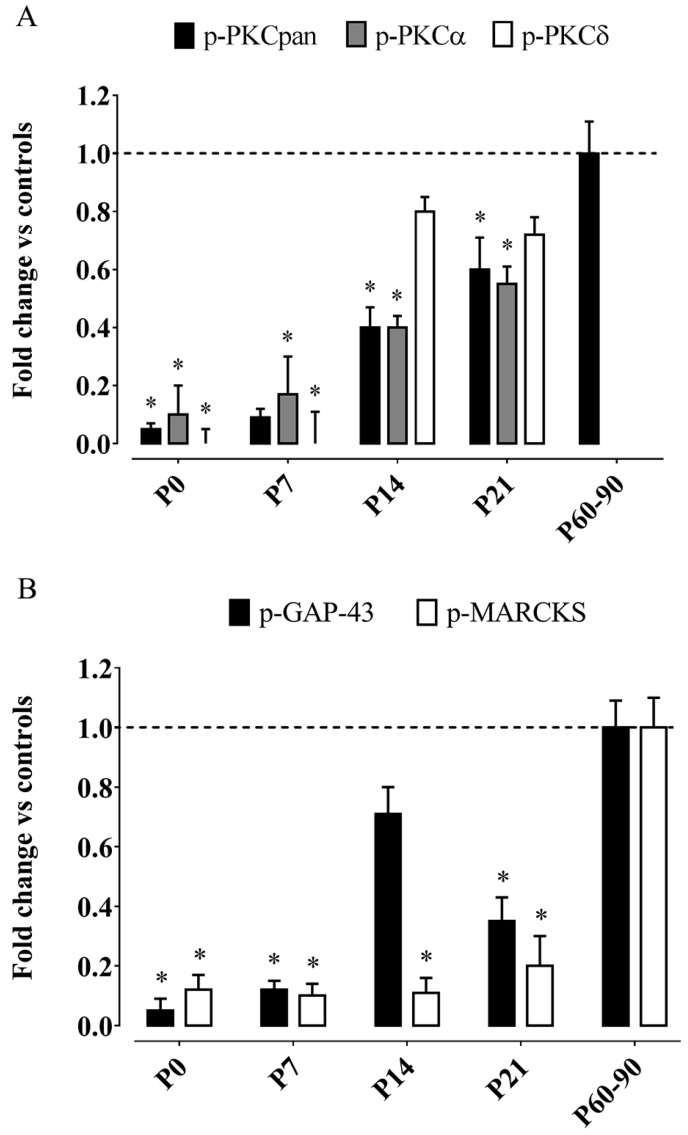
Figure 1.
Phosphorylation of protein kinase C (PKC) and PKC substrates are reduced in developing hippocampus of α-tocopherol-exposed pups. (A) PKCpan, PKCα and PKCδ phosphorylation in the hippocampus of developing offspring and PKCpan phosphorylation in the hippocampus of adult offspring; (B) Phosphorylation of PKC substrates GAP-43 and MARCKS in the hippocampus of developing and adult offspring. Hippocampal protein extracts taken from CTRL and TREAT developing and adult offspring (at each time point, for each group, n = 8 animals from four different litters) were subjected to SDS/PAGE (12% polyacrylamide for PKCpan, PKCα, PKCδ and GAP-43 and 7% polyacrylamide for MARCKS) followed by Western blotting, using polyclonal phospho-specific antibody directed to PKCpan, PKCα, PKCδ, GAP-43 and MARKS. Histograms represent densitometric analyses of blots from three independent experiments (means ± S.E.M.). Representative CTRL value is shown as dashed line. Relative decreases in band absorbance values (arbitrary units) were normalized for the control band in each series. Student’s t test: * p < 0.05. Figure modified from [78]. GAP: growth associated protein; MARCKS: myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate; CTRL: control, untreated; TREAT: treated.