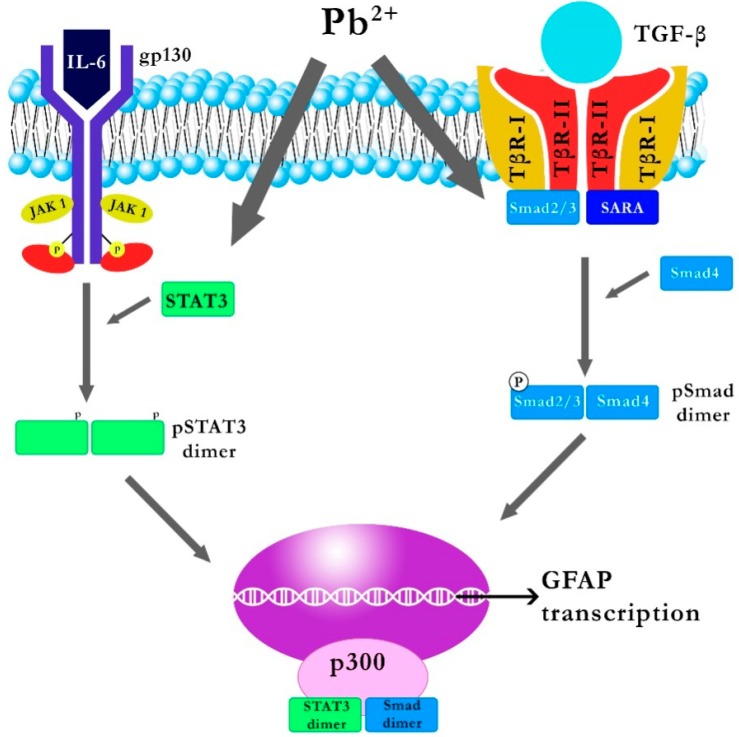
Figure 2.
Explanation of the likely impact of Pb on the IL-6 and TGF-β1 signal transduction pathways [22]. STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription; JAK1: Janus kinase 1, GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein, Smad: receptor-regulated protein. By annealing/binding to its receptor IL-6 Rα, IL-6 activates JAK associated with the membrane gp-130, which results in the phosphorylation of tyrosine on gp-130 which then recruits molecules such as signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). When connected to gp-130, STAT3 is phosphorylate by Janus kinase (JAK kinase), which results in the dimerization of STAT3 and translocation to the nucleus, where, by combining with the appropriate DNA sequences, it influences the expression of multiple genes. Binding of TGF-β to TβRII activates its kinase subunit, increases affinity to TβRI, and consequently the activation of TβRI which stimulates the phosphorylation of receptor-regulated protein Smad-3 bound to 3-endosomal SARA. The phosphorylated Smad-3 forms a heterodimer with Smad-4, and the resulting complex is transported to the nucleus, where it combines with CAGAC sequences or sequences rich in GC pairs in the promoter regions of many genes.