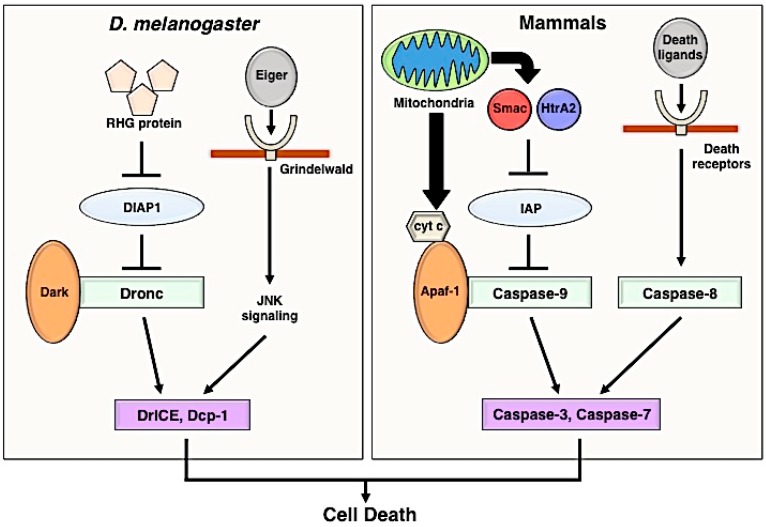
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the apoptosis signaling pathway in Drosophila and mammals. The same colors and shapes represent functional homologous in both Drosophila melanogaster and mammals. In Drosophila, RHG proteins (Rpr, Hid, and Grim) produced by apoptotic stimuli inhibit the function of DIAP1 (Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1). Dark (apaf-1 homologue) forms a complex (apoptosome) with the initiator caspase Dronc. Effector caspases DrICE and Dcp-1 are activated by the apoptosome, and the activated effector caspases promote cell death. Eiger (Drosophila TNFα ortholog) induces the JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase)-mediated cell-death pathway through Grindelwald (TNF receptor). In mammals, Smac and HtrA2 released from mitochondria block the function of IAP (Inhibitor of apoptosis protein). Mitochondria also secretes cytochrome c (cyt c), and the apoptosome which is consisted of cyt c, Apaf-1, and pro-caspase-9 activates effector caspases, such as Caspase-3 and Caspase-7. Cell death via initiator caspase-8 requires the activation of death ligands and receptor signaling (TNFα-TNF receptor and Fas-Fas ligand). TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α.