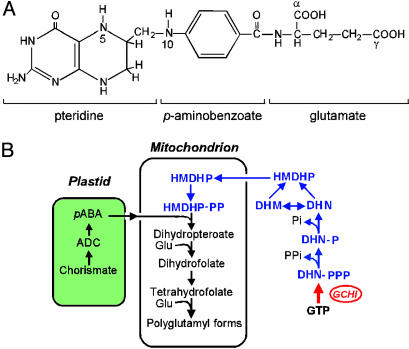
Fig. 1.
Structure and biosynthesis of folates. (A) Chemical structure of THF, monoglutamyl form. Most plant folates have γ-linked polyglutamyl tails of up to approximately six residues attached to the first glutamate. One-carbon units at various levels of oxidation (from formate to methyl) are attached to N-5 and/or N-10. The pteridine ring of folates and free pteridines can exist in tetrahydro, dihydro, and fully oxidized forms. (B) Outline of the plant folate synthesis pathway. Pteridines are in blue; note that one enzyme, dihydroneopterin (DHN) aldolase, interconverts dihydroneopterin and dihydromonapterin (DHM) and cleaves both to 6-hydroxymethyldihydropterin (HMDHP) (15). The red arrow is the engineered GCHI reaction. ADC, aminodeoxychorismate; -P, monophosphate; -PP, pyrophosphate; -PPP, triphosphate.