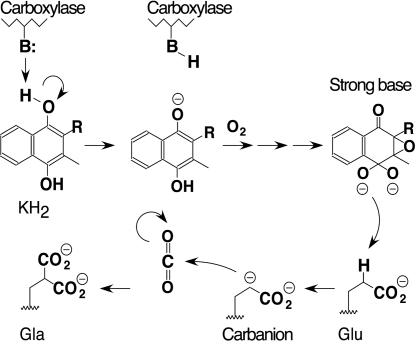
Fig. 1.
The base amplification model for carboxylation. The model proposes that a weak base (B:) in the carboxylase active site deprotonates KH2, resulting in KH2 oxygenation and formation of a strong base intermediate. The strong base deprotonates the γ-carbon of a substrate Glu side chain to generate a carbanion intermediate, which subsequently reacts with CO2 to form the Gla product. Protonation of the strong vitamin K base results in formation of a vitamin K epoxide product, which is not shown.