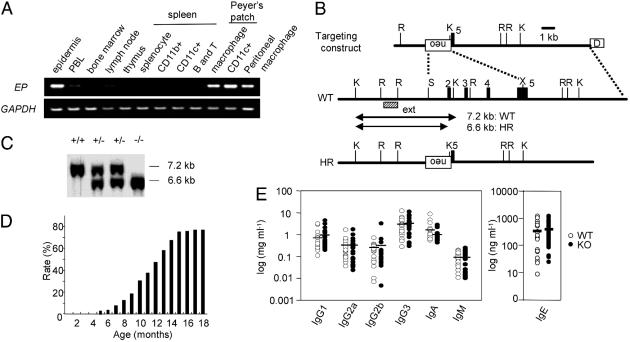
Fig. 1.
EP expression in mouse immune-related tissues and generation of EP-deficient mice. (A) EP expression level was determined by using RT-PCR with GAPDH as control. PBL, peripheral blood lymphocytes. (B) Schematic representations of targeting construct, WT EP genomic DNA, and homologous recombinant (HR) allele. The numbers denote exons (filled boxes). External probe (ext) used in Southern blot to detect HR events is indicated by a dashed box. The germ-line and recombinant KpnI restriction fragments are denoted by lines with arrowheads. Restriction sites: K, KpnI; R, EcoRI; S, SalI; X, XhoI; neo, pGK-neo; D, diphtheria toxin A fragment. (C) Southern blot of KpnI-digested genomic DNA with the external probe. (D) The rate of chronic dermatitis observed in EP–/– mice. (E) Serum Ig isotype concentration. Serum Ig isotype concentration was determined by ELISA. WT mice (open circles; n = 22) and EP–/– mice without dermatitis (filled circles; n = 20) at the age of 4 months. Mean values are indicated by short horizontal lines.