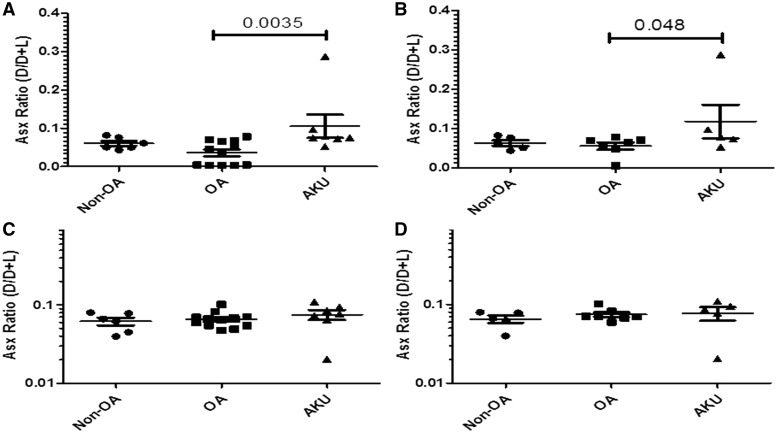
Fig. 5.
Racemized Asx content in PBS and insoluble extract alkaptonuric cartilage vs OA and non-OA
Graphs showing the amount of racemized Asx (D form) as a proportion of non-racemized Asp (L form) represented by the D/D+L ratio in AKU, OA and non-OA cartilage specimens. (A) Asx ratio (D/D+L) in PBS extract of all samples: both hips and knees from AKU (n = 6), OA (n = 12) and non-OA (n = 6) independent cartilage specimens. (B) Asx ratio (D/D+L) in PBS extract from hip-only samples from AKU (n = 4), OA (n = 7) and non-OA (n = 5) independent cartilage specimens. (C) Asx ratio (D/D+L) in insoluble extract of all samples: both hips and knees from AKU (n = 6), OA (n = 12) and non-OA (n = 6) independent cartilage specimens, (D) Asx ratio (D/D+L) in insoluble extract from hip-only samples from AKU (n = 4), OA (n = 7) and non-OA (n = 5) for independent cartilage specimens. Error bars represent the mean of the n in each group ± 95% CI. AKU: alkaptonuria; racemized Asx: aspartate and asparagine; Asp: aspartate; D: dextrorotary (d-isomer); L: levorotary (l-isomer).