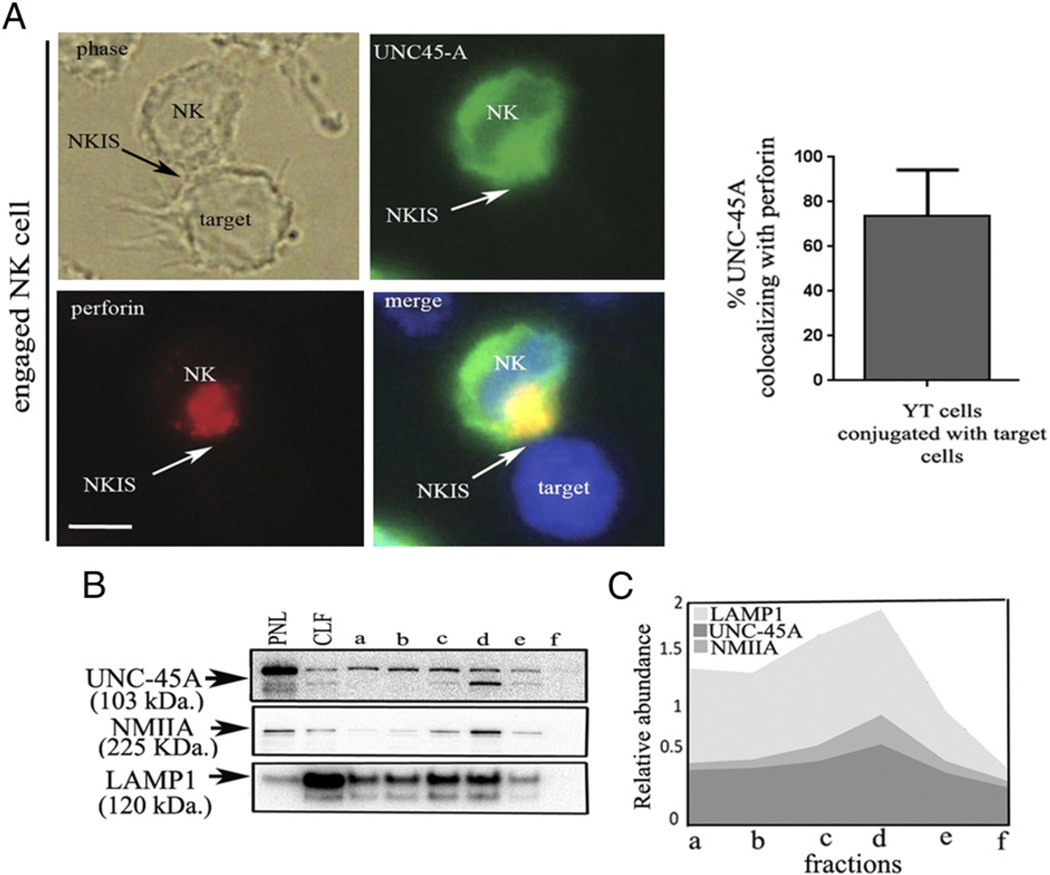
FIGURE 2.
UNC-45A colocalizes with perforin and interacts with lytic granules in engaged NK cells. (A, left panels) YT NK cells expressing a GFP–UNC-45A fusion protein were incubated in presence of 721.221 target cells for 30 min. After fixation and permeabilization, unengaged (left) or engaged (right) NK cells were stained with anti-perforin Ab and Texas red-conjugated anti-mouse IgG and analyzed by phase-contrast and fluorescence microscopy. Arrows indicate NKISs. Scale bars, 5 µM. (Right panel) Quantification of the percentage of UNC-45A colocalizing with perforin out of the total present in YT cells. (B) Fractions from density gradient separation of lytic granules in YT NK cells from least dense (lane a) to most dense (lane f), PNL, and CLF were used for Western blot analysis with Abs against UNC-45A, NMIIA, and LAMP-1. (C) Quantification of relative abundance of UNC-45A, NMIIA, and LAMP-1 in NK cell-derived lysosomal fractions.