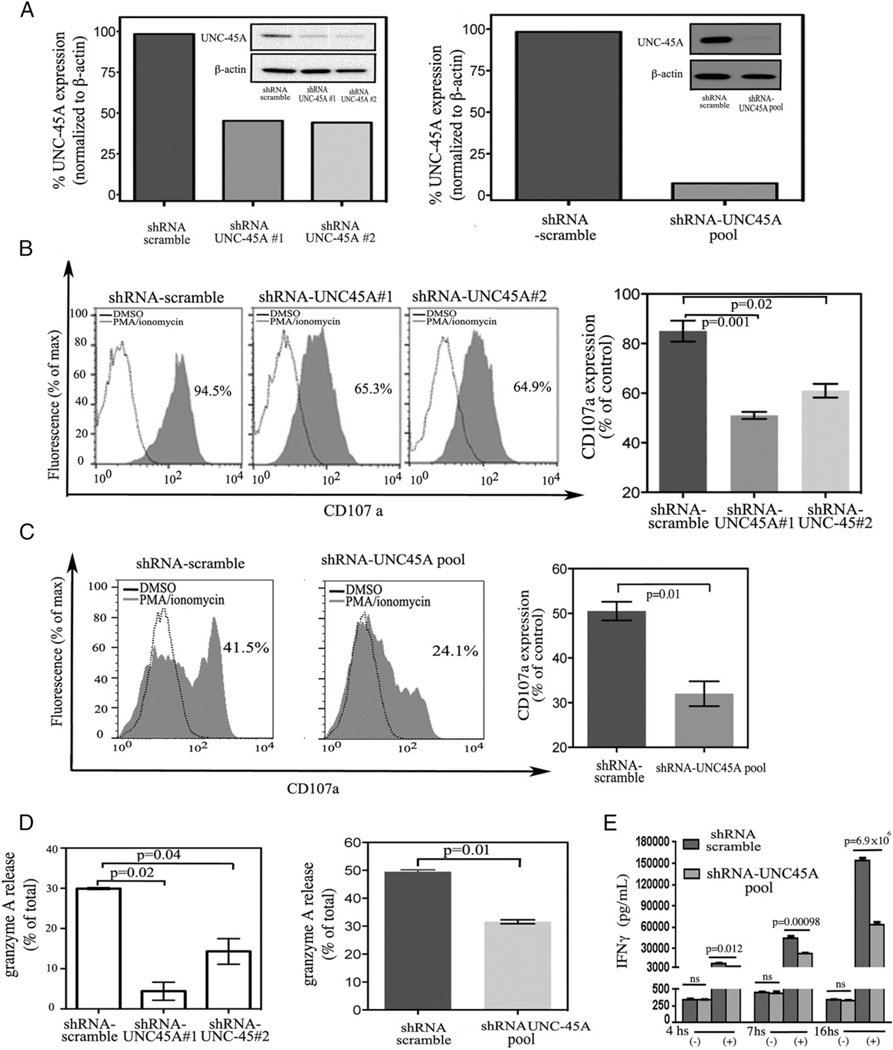
FIGURE 6.
UNC-45A knockdown prevents lytic granule secretion and IFN-γ release in NK cells. (A) UNC-45A protein expression levels in lysates of NKL (left panel) and NK-92 (right panel) cells upon transduction with either shRNA-scramble or shRNA targeting two different UNC-45A regions (1 and 2) and in NK-92 NK cells after transduction with shRNA scramble or shRNA consisting of a pool (shRNA-UNC-45A pool) of three 19- to 25-nt UNC-45A–specific shRNAs. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (B) NKL cells transduced with either shRNA-scramble or shRNA targeting two different UNC-45A regions (1 and 2) and either mock-treated (DMSO) or treated in presence of 25 ng/ml PMA and 0.5 µg/ml ionomycin. Surface CD107a expression was analyzed by FACS. A representative experiment is shown. (Right panel) Quantification of CD107a expression averaged from three independent experiments. (C, left panels) NK-92 cells transduced with either shRNA-scramble or shRNA consisting of a pool (shRNA-UNC-45A pool) of three 19- to 25-nt UNC-45A–specific shRNAs either mock-treated (DMSO) or treated in the presence of 50 ng/ml PMA and 0.5 µg/ml ionomycin. The effect of PMA/ionomycin stimulation on NK cells was evaluated by measuring the increase in surface expression of CD107a by FACS analysis. Representative experiment. (Right panel) Quantification of the CD107a expression. Average of three independent experiments. (Dleft panel) NKL cells transduced with either shRNA-scramble or shRNA targeting two different UNC-45A regions (1 and 2) and either mock-treated (DMSO) or treated in the presence of 25 ng/ml PMA and 0.5 µg/ml ionomycin. Granzyme A release is reported as the percentage of specific release over total enzymatic content. The average of three independent experiments is shown. (Right panel) NK-92 cells transduced with either shRNA-scramble or shRNA consisting of a pool (shRNA-UNC-45A pool) of three 19- to 25-nt UNC-45A–specific shRNAs were either mock-treated (DMSO) or treated in the presence of 50 ng/ml PMA and 0.5 µg/ml ionomycin. Granzyme A release is reported as the percentage of specific release over total enzymatic content. The average of three independent experiments is shown. (E) Scramble and UNC-45A knockdown (pool) NK-92 cells mock-treated (−) or stimulated in the presence of 10 ng/ml IL-12 and 100 ng/ml IL-18 (+) over a period of 4, 7, or 16 h. Per each condition, IFN-γ secretion was measured by ELISA and expressed as IFN-γ pg/ml.