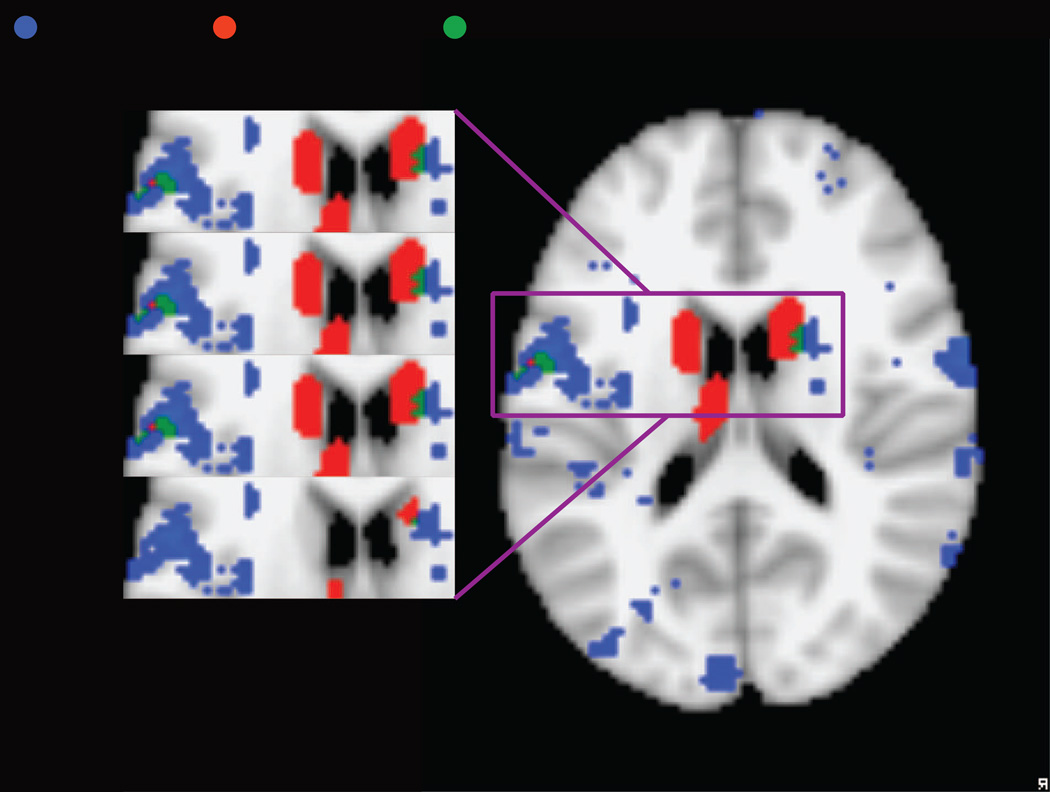
Figure 5.
(a) Comparison between cortical and cerebellar regions involved in articulatory processing (blue), identified using reverse inference with the Neurosynth database and cortical regions of increased activation in RD relative to typical readers (red) based on a manual meta-analysis of RD studies, with overlap in green. (b) Detail of overlap between subcortical and IFG/insula regions involved in articulatory processing (blue), identified using reverse inference with the Neurosynth database and cortical regions of increased activation in RD relative to typical readers (red) based on a manual meta-analysis of RD studies, with overlap in green. The results of the RD meta-analysis are presented at a voxel threshold of p < .05 to p < .001 to illustrate the stability of the overlap.