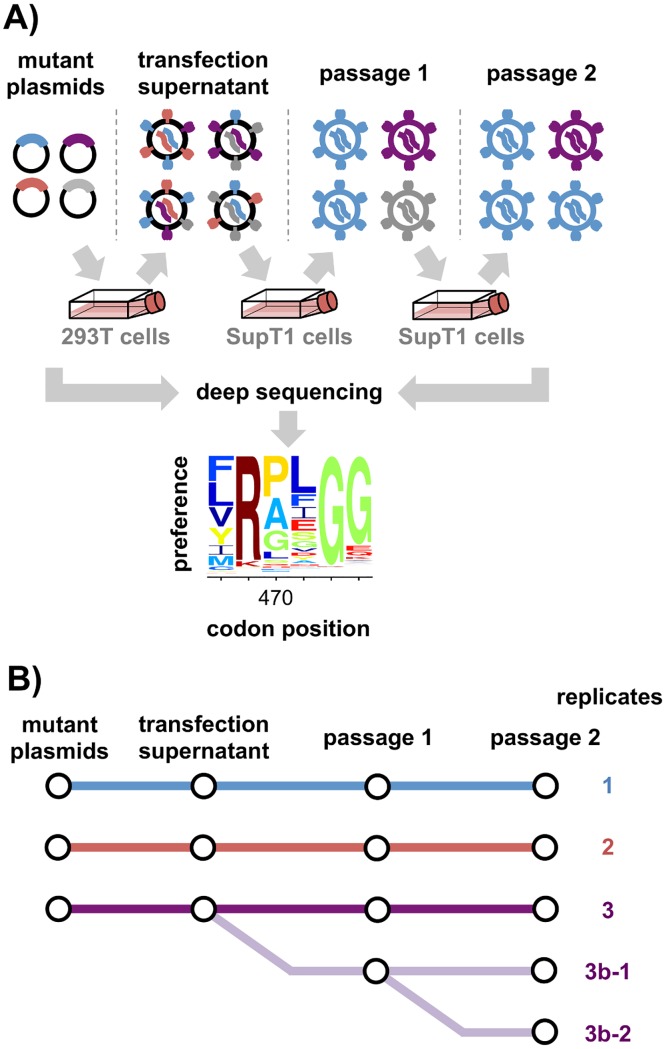
Fig 1. Deep mutational scanning workflow.
(A) We created libraries of HIV proviral plasmids with random codon mutations in env, and generated mutant viruses by transfecting these plasmid libraries into 293T cells. Since cells receive multiple plasmids, there may not be a link between viral genotype and phenotype at this stage. To establish this link and select for functional variants, we passaged the viruses twice at low multiplicity of infection (MOI) in SupT1 cells. We deep sequenced env before and after selection to quantify the enrichment or depletion of each mutation, and used these data to estimate the preference of each site for each amino acid. Each mutant library was paired with a control in which cells were transfected with a wildtype HIV proviral plasmid to generate initially wildtype viruses that were passaged in parallel with the mutant viruses. Deep sequencing of these wildtype controls enabled estimation of the rates of apparent mutations arising from deep sequencing and viral replication. (B) We performed the entire experiment in triplicate. Additionally, we passaged the replicate-3 transfection supernatant in duplicate (replicate 3b). We also performed the second passage of replicate 3b in duplicate (replicates 3b-1 and 3b-2).