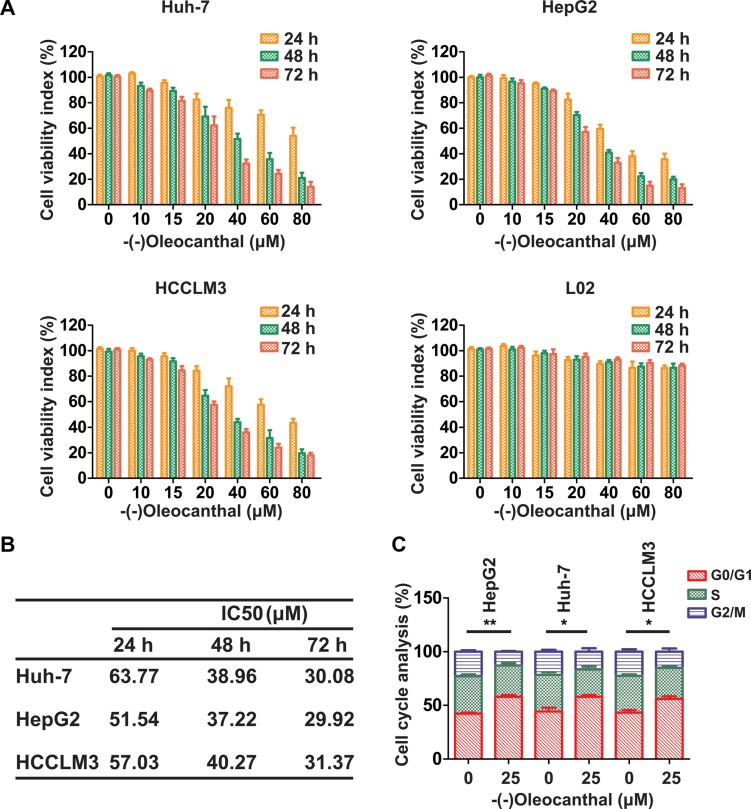
Figure 1. (−)-Oleocanthal inhibits proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest in HCC cells in vitro.
(A) HCC cell lines (Huh-7, HepG2 and HCCLM3) and human normal liver cell line (LO2) were incubated with increasing doses of (−)-oleocanthal (0-80 μM) for 24–72 h. Then, CCK-8 assay was performed to investigate the cell viability index. (B) The IC50 of (−)-oleocanthal was calculated in the three HCC cell lines. (C) Cell cycle analysis in (−)-oleocanthal-treated HCC cells showing arrest in G0/G1 phase. The results represent means ± SD of experiments performed in triplicate. * compared with control, P < 0.05. ** compared with control, P < 0.01.