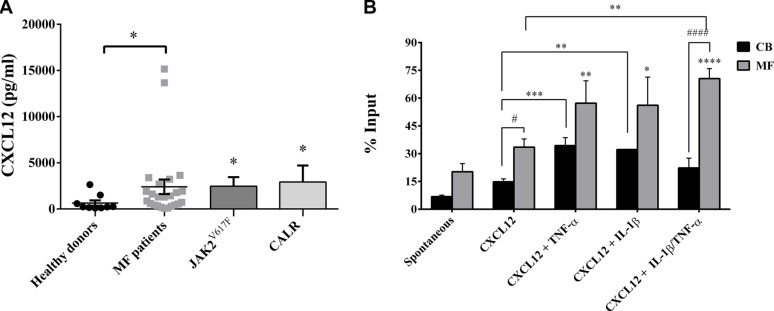
Figure 6. IL-1β and TNF-α significantly increases migration of MF-derived CD34+ cells.
(A) CXCL12 plasma levels of MF patients (total n =24; JAK2V617F mutated patients n = 16; CALR mutated patients n = 8) and controls (n = 10). Regardless mutation status, CXCL12 concentration was significantly higher in MF patients (*p ≤ 0.05 vs controls). (B) When cells were migrated toward CXCL12 alone, an increased migration ability was observed in MF-derived (n = 15) CD34+ cells as compared with the CB-derived (n = 8) counterparts. The addition of inflammatory factors alone (IL-1β/TNF-α) plus CXCL12 significantly increased the migratory behaviour of MF-derived CD34+ cells as compared with CXCL12 alone. IL-1β + TNF-α synergistically enhanced the migratory behaviour of CD34+ cells as compared with spontaneous migration (****p < 0.0001), CXCL12 alone (**p <0.001) and the CB-counterpart (####p <0.0001). Results are expressed as mean percentages ± SEM of input. (**p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001 vs CXCL12 alone for CB-derived CD34+ cells) (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ****p < 0.0001 vs spontaneous migration for MF-derived CD34+ cells) (#p ≤ 0.05; ####p <0.0001 vs CB).