Figure 1. MM1 binds to C-terminus of p63α.
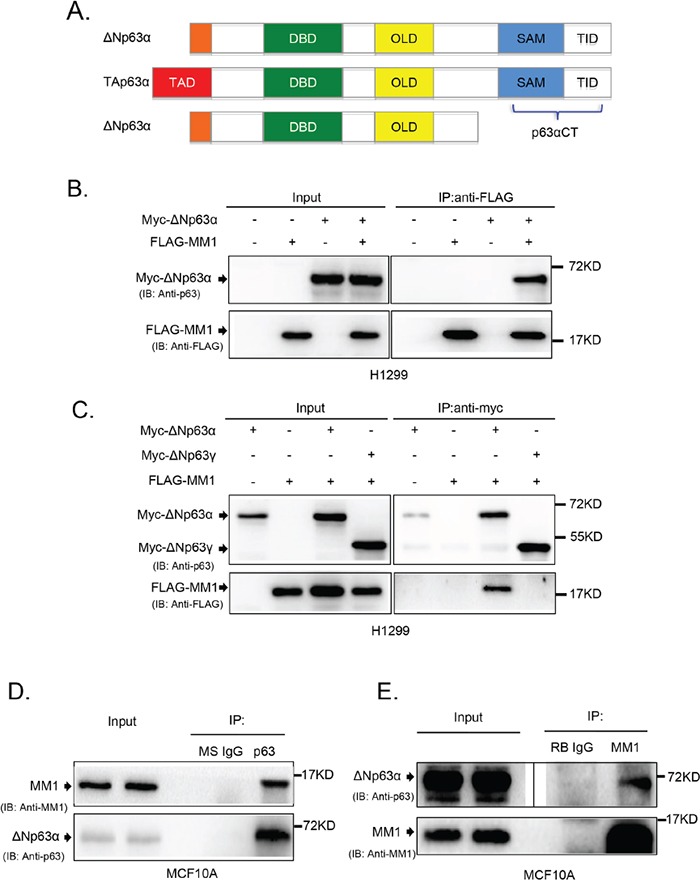
A. Schematic structure of p63 protein isoforms. TAD: transactivation domain; DBD: DNA-binding domain; OLD: oligomerization domain; SAM: sterile alpha motif; TID: transinhibitory domain. The C-terminal fragment of p63α (p63αCT), containing SAM and TID regions, was cloned as a “bait” for yeast two-hybrid screening. B. and C. ΔNp63α, but not ΔNp63γ, binds to MM1 in transfected cells. H1299 cells were co-transfected to express Myc-tagged ΔNp63α or ΔNp63γ plus FLAG-tagged MM1 proteins. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with antibody to FLAG or Myc tag. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-p63 and anti-FLAG. Whole cell lysates were used as input controls. D. and E. Endogenous proteins of ΔNp63α and MM1 form stable complexes. MCF10A cell lysates were subjected to IP with anti-p63 or anti-MM1, using normal mouse IgG (MS IgG) or normal rabbit IgG (RB IgG), respectively, as a control. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by IB with anti-p63 and anti-MM1. Whole cell lysates were used as input controls. Image of either short or long exposure was shown for ΔNp63α bands.
