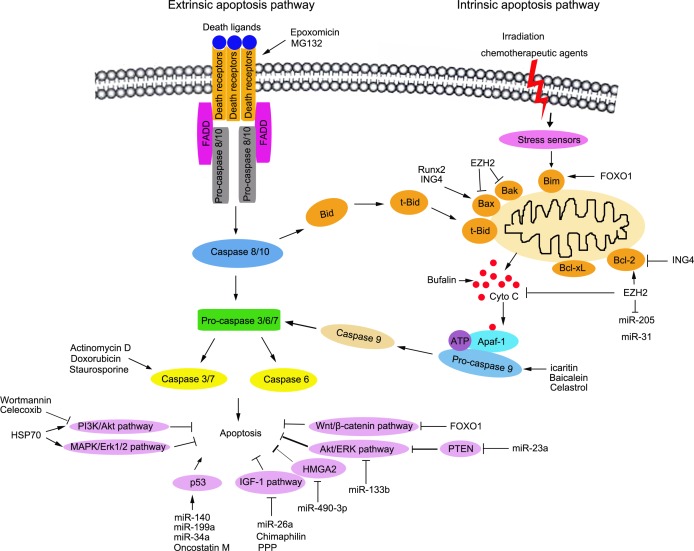
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the signalling pathways to apoptosis and the regulation of apoptosis in osteosarcoma therapy.
The two major apoptosis signaling pathways to induce apoptotic cell death are shown: extrinsic (death receptor mediated) apoptosis pathways and intrinsic (mitochondrial mediated) apoptosis pathways. In extrinsic pathway, cell apoptosis is initiated by binding of death ligands and death receptors. Next, the death-inducing siganalling complex (DISC) is assembled and caspase-8/10 is activated. In intrinsic apoptosis pathway, cell apoptosis is induced by a variety of intracellular stimuli, including damages, growth factor deprivation or oxidative stress. The cytochrome C is released from the mitochondria resulting in the formation of the apoptosome and activation of caspase-9. The activated caspase-8 and 9 trigger the execution of apoptosis by activating the downstream caspase-3, 6 and 7. It has been reported in the literature, the agents, such as natural compounds, miRNA and proteins are effective to promote or block cell apoptosis in treatment of osteosarcoma.