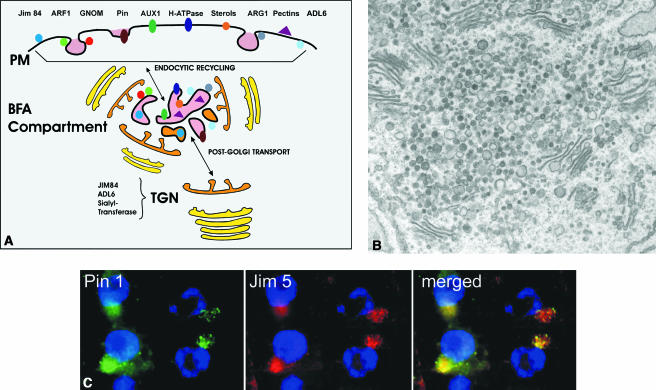
Figure 2.
A, Endocytosis in plants—insights from BFA compartments. Upon BFA treatment, the following plasma membrane and plasma membrane-associated molecules accumulate in BFA compartments: PINs (putative auxin efflux carriers), AUX1 (putative auxin influx carrier), plasma membrane H-ATPase, plasma membrane structural sterols, and peripheral membrane protein ARG1 (altered response to gravity). Except this, cell wall pectins cross-linked by boron, small GTPase ARF1, and ARF activator GNOM (ARF-GEF) accumulate within BFA compartments. The JIM84 carbohydrate epitope and dynamin ADL6 associate both with plasma membrane and TGN, and can be eventually transported to the BFA compartment from both locations. Internalization of cell wall pectins could be inhibited by short-term boron deprivation. AUX1 accumulation to BFA compartments is restricted to protophloem cells. B, Ultrastructure of BFA compartment after 30-min incubation of root epidermal cell with 25 μm BFA (reproduced with permission from Grebe et al., 2003). C, Immunofluorescence colocalization of putative auxin efflux carrier PIN1 (second antibody coupled to FITC; green) and cell wall pectins recognized by monoclonal antibody JIM5 (secondary antibody coupled to TRITC; red) on BFA compartments (yellow) in maize root cells treated with 100 μm BFA for 2 h. Nuclei (blue) are counterstained with DAPI.