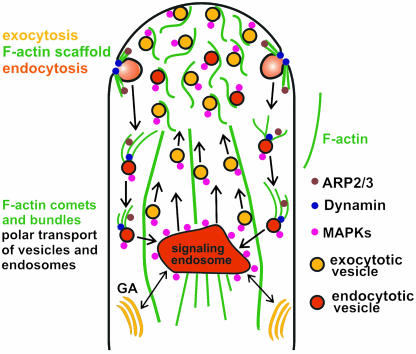
Figure 3.
Working model depicting endosomal/vesicular trafficking and possible roles of the actin filaments in an idealized tip-growing root hair. Local actin polymerization together with accumulation of dynamin could facilitate endocytic recycling of receptors, ion channels, and cell wall molecules (e.g. pectins and AGPs) by assisting the pinching off the endocytic vesicles and by forming actin comets on these vesicles dependent on ARPs. Signaling molecules such as MAPKs associate both with endosomal vesicles and the actin cytoskeleton. Additionally, dense meshworks of actin filaments regulated by profilins and ARPs are suggested to act as a structural scaffold in order to sequester and maintain signaling and regulatory molecules, including MAPKs within the apical vesicle pool (clear zone). GA, Golgi apparatus. Arrows indicate polar trafficking of exo- and endocytic vesicles/endosomes, as well as putative transport between TGN and endosomes.