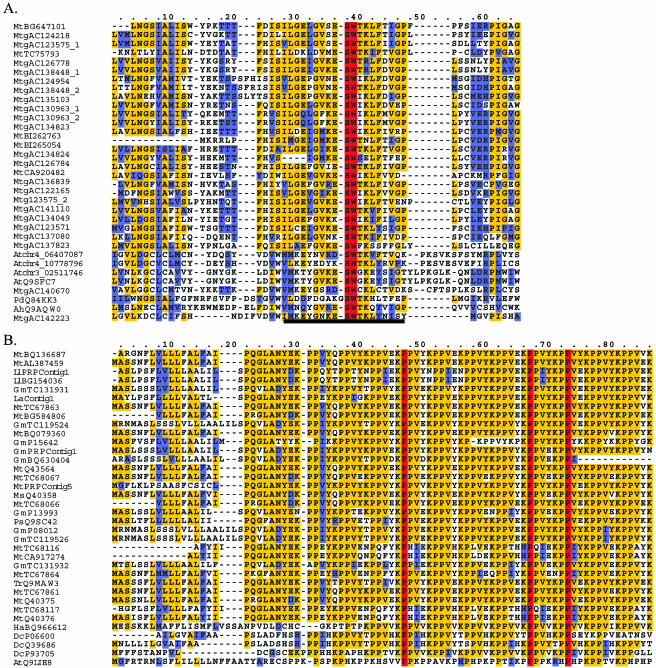
Figure 1.
Motif analysis of clustered sequences reveals similarity to F-box-associated domains and Pro-rich proteins. Residues that are identical throughout the proteins are shown in red. Residues conserved in more than 50% of the proteins are shown in yellow. Similar amino acid residues are shown in blue. Gaps (-) were introduced to optimize the alignments. Given the large number of sequences in the alignments, not all sequences are shown. All sequence names are preceded by a two-letter abbreviation representing the species name: At (Arabidopsis), Pd (Prunus dulcis), Ah (Antirrhinum hispanicum), Ll (L. luteus), La (L. albus), Ms (M. sativa), Ps (pea), Ha (sunflower), and Dc (carrot). Mt (GenBank accession) and Gm (GenBank accession) refer to EST singletons from M. truncatula and G. max/soja, respectively. MtTC and GmTC refer to TCs from M. truncatula and G. max/soja, respectively. Mtg (GenBank accession) refers to M. truncatula genomic sequence. Atchr (number) refers to unannotated Arabidopsis chromosomal sequence. The approximate position of the predicted start site follows the underscore. This number is based on the analysis of the Arabidopsis genome sequence (TIGR 3.0). A, Motif analysis of group 640 revealed similarity to a core 20 amino acid region within the larger F-box-associated domain. This region has been underlined. The alignment demonstrates the variability found outside this core domain. Sequences PdQ84KK3, AtQ9SFC7, and AhQ9AQW0 were identified from Swiss-Prot/TrEMBL. B, Regular expression pattern analysis of group 5 revealed similarities to Pro-rich cell wall proteins. LlPRPContig1, LaPRPContig1, GmPRPContig1, and MtPRPContig5 represent contigs assembled using the Sequencher software. GmP15642, GmP13993, GmP08012, MtQ43564, MtQ40375, MtQ40376, MsQ40358, PsQ9SC42, DcP06600, DcQ39686, DcP93705, and AtQ9LIE8 were identified from Swiss-Prot/TrEMBL.