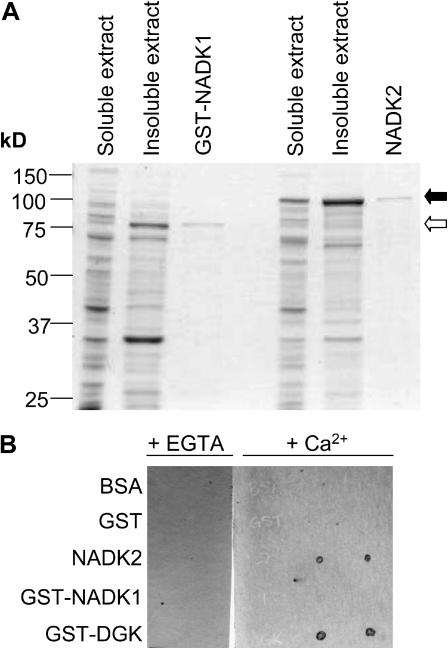
Figure 2.
Expression and purification of recombinant NADK1 and NADK2 and identification of NADK2 as a CaM-binding protein. A, NADK1 was expressed as a GST-fusion protein (GST-NADK1) and purified from the soluble extract of E. coli lysates using GSH-affinity chromatography. NADK2 was expressed as an untagged protein and purified from the soluble extract of E. coli lysates using CaM-affinity chromatography as described in “Materials and Methods.” Open and closed arrows indicate the migration positions in SDS-PAGE gels for GST-NADK1 and NADK2, respectively. A Coomassie Blue-stained gel showing 20.0 μg of soluble and insoluble bacterial extract and 1.0 μg of each purified recombinant protein from a typical purification is presented. B, An overlay spot-blot assay using fluorescently labeled recombinant CaM81 as a probe, in the presence of either 1 mm CaCl2 (+Ca2+) or 10 mm EGTA (+EGTA), was used to examine the CaM-binding abilities of NADK1 and NADK2. Purified, recombinant, nondenatured proteins (50 ng) were spotted (in duplicate) onto nitrocellulose, blocked in 25 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, containing 5% (w/v) nonfat milk in the presence of either CaCl2 or EGTA and then incubated with 110 nm fluorescently labeled CaM81. After washing the blots, CaM-binding proteins were detected by fluorescent imaging. A GST-fusion protein containing the CaM-binding domain of a tomato diacylglycerol kinase (GST-DGK) was used as a positive control, whereas GST and bovine serum albumin (BSA) served as negative controls.