Figure 1.
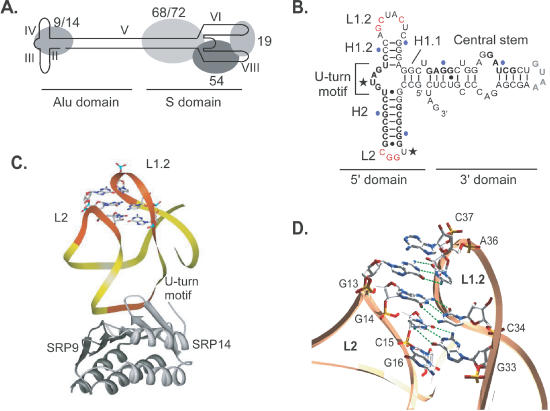
Structure of SRP and the SRP Alu domain. (A) Schematic representation of SRP, (B) secondary structure of the minimal Alu RNA that still binds 9/14 efficiently. Stems and loops are named according to the topological nomenclature. Bases in the loops that form tertiary base pairs are highlighted in red. Protein footprints are shown in boldface. U-turns are marked with asterisks and stretches of 10 nt are marked in blue. The U-turn motif marks a highly conserved sequence that represents the major protein-binding site. (C) Structure of the SRP Alu 5′ domain. SRP9 and SRP14 are displayed as dark and light grey ribbons, respectively. The RNA is shown as a yellow ribbon with the loop sequences and the U-turn motif shown in orange. Nucleotides from loops L2 and L1.2 that are involved in tertiary interactions between the loops are shown as wireframe. (D) Detailed view of the tertiary base pairing between loops. Bases G13, G14 and C15 form hydrogen bonds with C37, C34 and G33, respectively (dotted green lines). One base from each loop, G16 and A36, are positioned to extend the stack formed by the three base pairs.
