Figure 1.
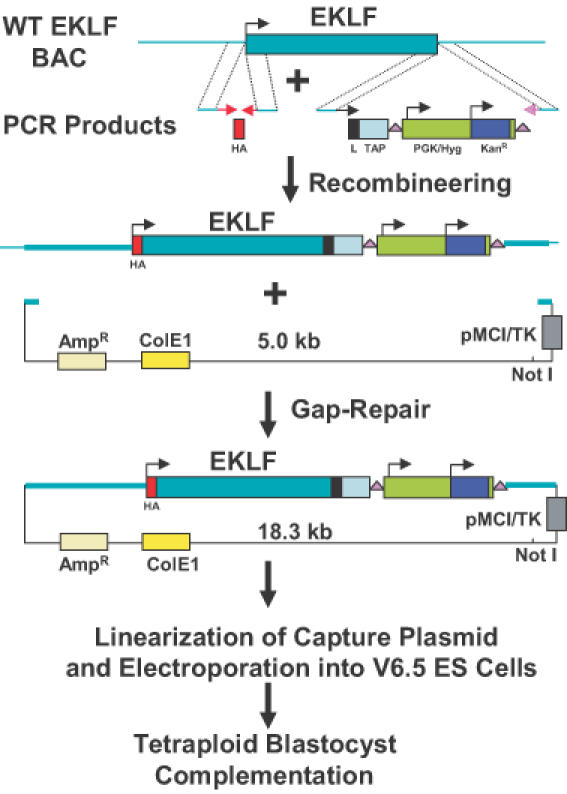
Overview of method. A BAC clone containing the EKLF gene was transferred from the E.coli strain DH10B to the recombineering strain DY380. These cells were electroporated with PCR products containing an HA tag and a TAPR (Linker/TAP/loxP-PGK/Hyg/KanR-loxP) cassette flanked by 60–79 bp EKLF homologies. Cells containing the correctly modified BAC were electroporated with a PCR product containing AmpR, ColE1 and herpes simplex virus (HSV) thymidine kinase sequences flanked by 50 bp homologies. By GR, this fragment rescued a 13.3 kb fragment containing the modified EKLF gene plus 6 kb of upstream sequence and 1 kb of downstream sequence. The resulting 18.3 kb plasmid was linearized with NotI and electroporated into the F1 hybrid (B6/129) ES cell line, V6.5. Hygromycin and gancylovir-resistant colonies were analyzed for homologous recombination by PCR and Southern blot hybridization. Correctly targeted ES cells were subsequently injected into tetraploid blastocysts to clone mice that are heterozygous for the tagged EKLF gene, HA–EKLF–TAP.
