Figure 4.
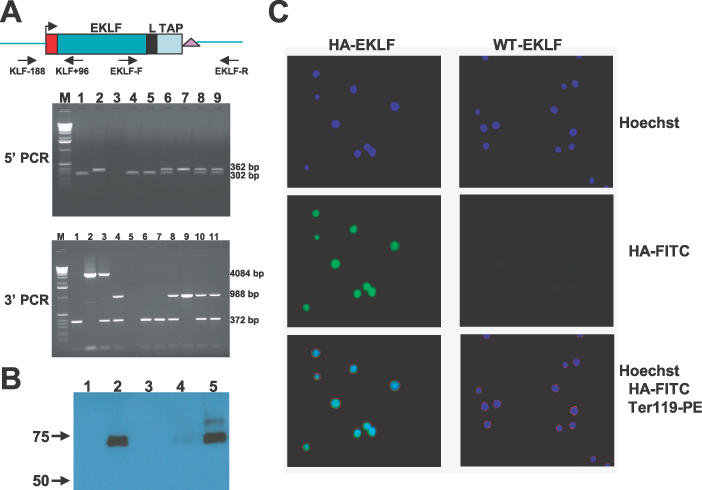
HA–EKLF–TAP expression in homozygous HA–EKLF–TAP mice. (A) PCR amplification of mouse tail DNA. For 5′ PCR, the predicted products for wild-type and HA–EKLF–TAP alleles are 302 and 362 bp, respectively. For 3′ PCR, the predicted products for wild-type and HA–EKLF–TAP alleles before CRE deletion are 372 and 4084 bp, respectively. After CRE deletion, the HA–EKLF–TAP allele is 988 bp. For 5′PCR, lane M, 1.0 kb marker; lane 1, wild-type C57B6 mouse; lane 2, modified EKLF BAC DNA; lane 3, primer control; lanes 4–9, individual pups in a single litter produced by mating heterozygotes. For 3′ PCR, lane M, 1.0 kb marker; lane 1, wild-type C57/B6 mouse; lane 2, modified EKLF BAC DNA; lane 3, a cloned heterozygous mouse; lane 4, a heterozygous mouse in which the PGK/Hyg/KanR markers have been removed by Cre recombinase; lane 5, primer control; lanes 6–11, same litter as above. (B) Western blot with anti-HA antibody. Whole-cell extracts were used in western blot. Lane 1, COS cells transfected with a control plasmid, pSG5; lane 2, COS cells transfected with an HA–EKLF–TAP cDNA plasmid, pDZ17; lane 3, Ter119+ bone marrow cells from a wild-type mouse; lane 4, Ter119− bone marrow cells from an HA–EKLF–TAP homozygous mouse; lane 5, Ter119+ bone marrow cells from an HA–EKLF–TAP homozygous mouse. (C) Fluorescent digital sections of Ter119+ bone marrow cells from a wild-type mouse and an HA–EKLF–TAP homozygous mouse stained with Hoechst, anti-HA monoclonal antibody conjugated with FITC and anti-Ter119 monoclonal antibody conjugated with PE.
