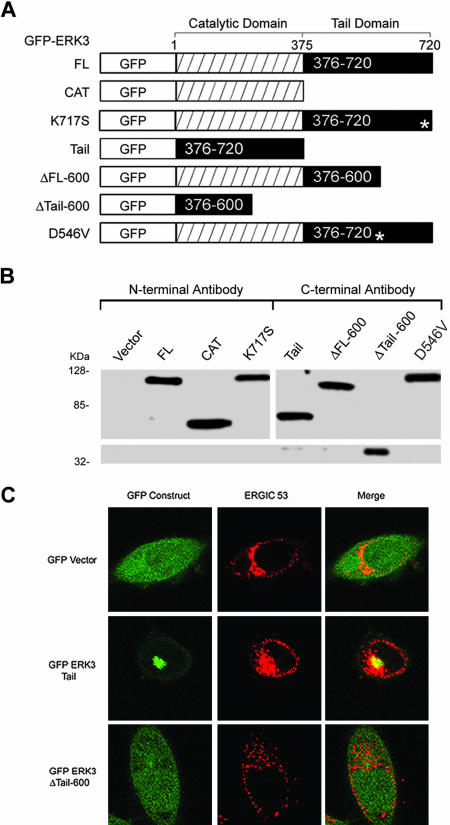
Figure 4.
The ERK3 carboxy terminus defines a Golgi/ERGIC targeting domain. (A) Amino-terminally GFP-tagged portions of the rat ERK3 open reading frame were created and expressed. All constructs that include the catalytic domain (GFP-ERK3 FL, ERK3 CAT, ERK3 ΔFL600, ERK3 K717S, and ERK3 D546V contain a FLAG epitope 3′ to the GFP open reading frame and 5′ to the ERK3 initiator methionine). Asterisks in the tail domains of the K717S and D546V mutants indicate positions of the mutations in the protein. The GFP-ERK3 tail construct (376–720) and the GFP-ERK3 Δtail600 (376–600) are direct fusions of the designated ERK3 sequence with GFP and contain no other intervening sequence. The GFP-ERK3 Δ383–398, GFP ERK3 Δ383–398/D546V, and GFP-ERK3 Δ KHLN have not been represented schematically here but were constructed in exactly the same way as the GFP-ERK FL construct. These expression vectors all contain a FLAG epitope 3′ to the GFP open reading frame and 5′ to the initiator methionine. (B) Immunoblots of GFP-ERK3 fusion proteins produced by transient expression in HEK 293 cells. Lanes 1–8 correspond to 50 μg of whole cell extracts prepared from cells transfected with the indicated vectors (A). Lanes 1–4 of the immunoblot were probed with the N-terminal anti-ERK3 antibody. Lanes 5–8 were probed with the C-terminal anti-ERK3 antibody. (C) HeLa cells were electroporated with the control GFP vector, GFP-ERK3 tail, or GFP-ERK3 Δ tail 600, plated onto coverslips, and then fixed after 24 h. The cells were then stained with anti-ERGIC-53 (G1/93) mAb.