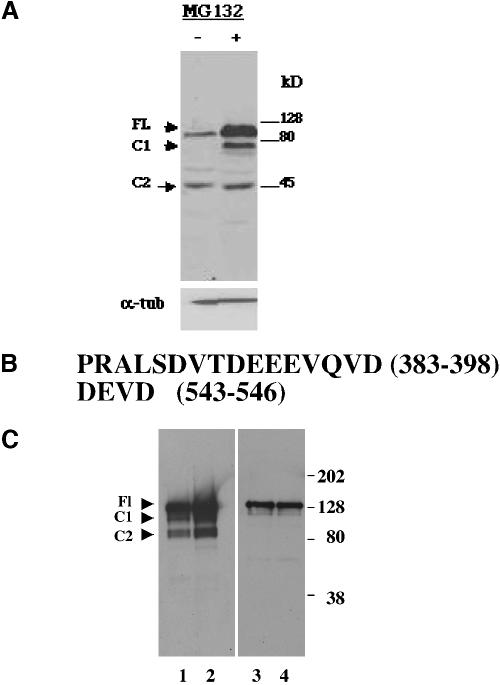
Figure 6.
Deletion of a carboxy-terminal acidic-rich region hinders ERK3 exit from the Golgi/ERGIC. (A) Immunoblot of whole cell extracts prepared from exponentially growing HeLa cells incubated in 10 μM MG132 for 3 h (5-min exposure of the film). Protein (50 μg) was loaded in each lane. The upper blot was probed with C-terminal anti-ERK3 antibody. Protein normalization of all the samples (50 μg/lane; bottom) was confirmed by probing a Western blot of total cell lysates with an anti-α tubulin antibody (lower blot). (B) Amino acid sequences of the two mutant regions tested as putative cleavage sites. A 15-nucleotide sequence immediately 5′ to the nucleotides encoded for the region of interest (amino acids 388–98) also was deleted because it contained a unique enzymatic restriction site that aided in the identification of bacterial colonies expressing this recombinant plasmid. Thus, all constructs containing the Δ383–398 deletion lack the sequence PRALS immediately amino-terminal to DVTDEEEVQVD (amino acids). (C) Immunoblot of FLAG immunoprecipitations of extracts of HeLa cells transiently expressing various forms of GFP-ERK3. To normalize for differences in level of protein expression, 1 mg of protein was used for the GFP-ERK3 Δ383–398 and GFP ERK3 Δ383–398/D546V immunoprecipitations and 200 μg of protein was used for the GFP-ERK3 FL and GFP-ERK3 D546V immunoprecipitations. The blots were probed with the C-terminal anti-ERK3 antibody. The expression constructs used for transfections in lanes 1–4 are, respectively, GFP-ERK3 FL, GFP-ERK3 D546V, GFP-ERK3 Δ383–398, and GFP ERK3 Δ383–398/D546V.