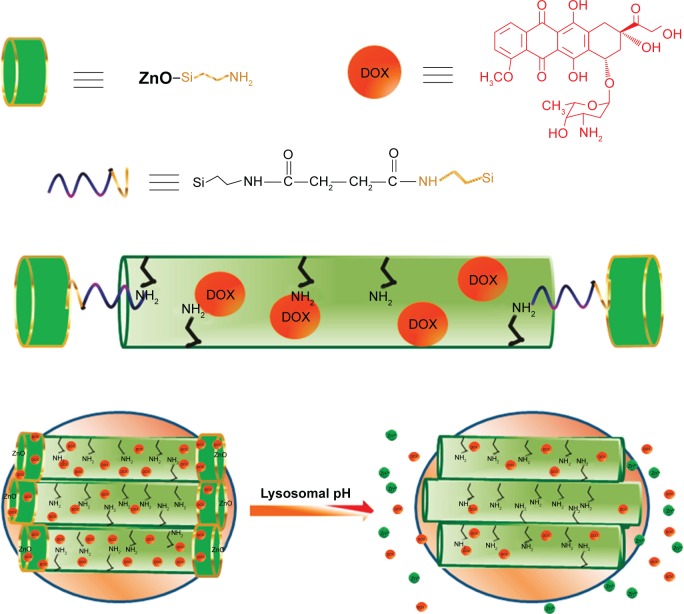
Figure 4.
Schematic illustration of the synthesis of ZnO@MSN-DOX and working protocol for pH-triggered release of the DOX from ZnO@MSN-DOX to the cytosol via selective dissolution of ZnO QDs in the acidic intracellular compartments of cancer cells.
Note: Reprinted with permission from Muhammad F, Guo M, Qi W, et al. pH-Triggered controlled drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles via intracelluar dissolution of ZnO nanolids. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(23):8778–8781. Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society.75
Abbreviations: MSN, mesoporous silica nanoparticle; DOX, doxorubicin hydrochloride; QDs, quantum dots.