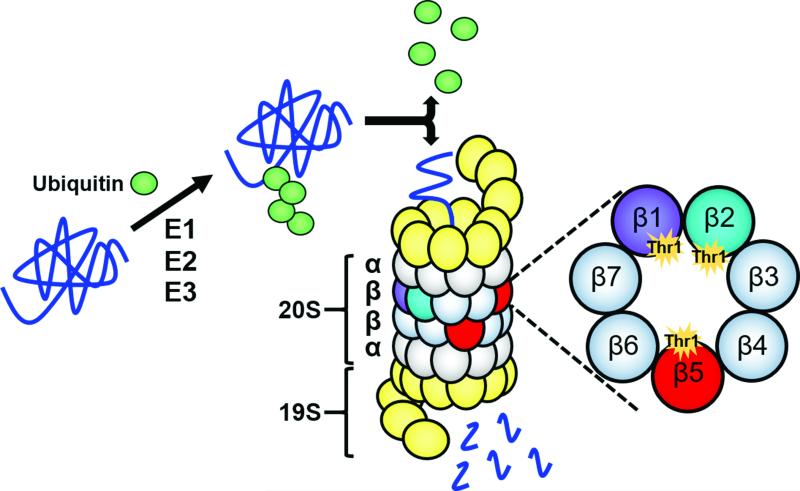
Figure 1.
The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway for protein degradation. A series of three enzymes – E1s, E2s, and E3s – assemble a polyubiquitin chain on a substrate protein to mark it for degradation by the proteasome. The polyubiquitin chain is recognized by the proteasome's 19S regulatory cap, which removes the chain and feeds the protein into the 20S proteasome core. Each of the two outer rings of the 20S core contains seven α subunits (α1-α7), while each of the two inner rings contains seven β subunits (β1-β7). Only β1, β2, and β5 are catalytically active; they contain active sites harboring catalytic N-terminal threonine (Thr1) residues. These three subunits work together to degrade the incoming protein to short peptides.