Figure 7.
Complementation of the sta7-10 Background with STA7 Genomic DNA.
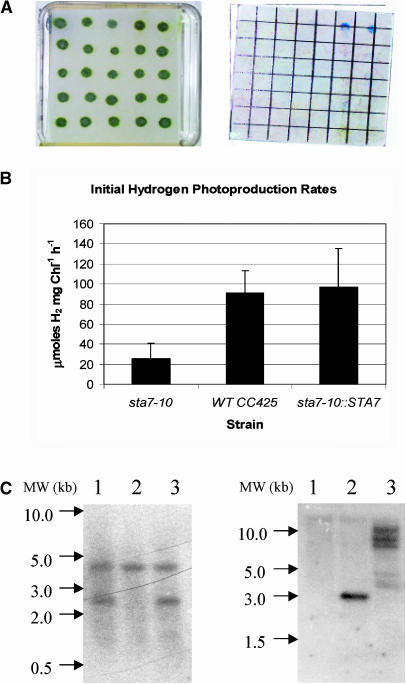
(A) Algal colonies on TAP plates after complementation with the STA7 gene (left) and chemochromic sensors after illumination (right).
(B) Hydrogen production rates.
(C) DNA gel blot analysis.
The chemochromic sensor (A) indicates that only two colonies at the far right of the first row are able to produce sufficient quantities of H2 for detection. These two clones were also the only colonies with wild-type levels of starch. Hydrogen-production rates (B) in solution measured using a Clark electrode apparatus. The mutant sta7-10 strain shows rates that are 20% to 40% those of the wild-type CC425. Mutant background complemented with STA7 (sta7-10::STA7) shows H2-production rates similar to CC425. DNA gel blot analysis of PstI-digested genomic DNA probed using the 130-bp /StuI-SphI fragment from the Arg7 gene ([C], left). DNA extracted from sta7-10, CC425, and sta7-10::STA7 cultures are shown in lanes 1, 2, and 3, respectively. DNA gel blot analysis of NotI-digested genomic DNA probed with the 114-bp KpnI-SacI fragment from the 3′ end of the genomic STA7 gene ([C], right). DNA samples are as described for the Arg7 blot.