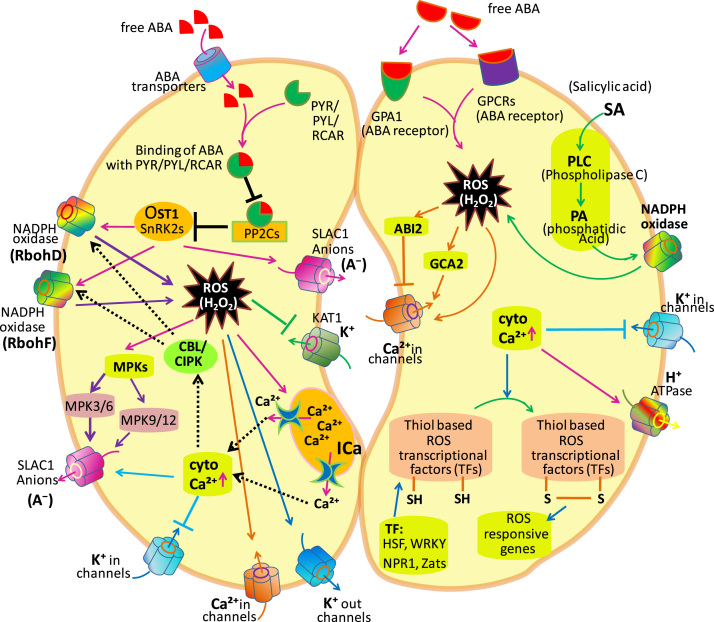
Fig. 1.
Targets of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in guard cells. The ROS with sensors play a key role in stomatal movement, which not only supervise ROS concentration in and out of the cell, but also respond to ROS signals. Here the abbreviations are; different channels: NADPH oxidase channels (RbohD and RbohF); S-type anion channel; SLAC1; calcium channels (Ca+in), potassium channels KAT1 (K+in channel), etc. Receptors; G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); ABA receptor (PYL/PYL/RCAR); type 2C protein phosphatase (PP2C); open stomata 1 (Ost1); Sucrose nonfermenting-related protein kinase 2 (SnRK2s); Arabidopsis α-subunit of the trimeric G protein (GPA1). Calcium dependent protein kinase; MPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MPK3/6, MPK9/12); Growth Controlled by Abscisic Acid 2 (GCA2); ABA insensitive 2 (ABI2); Ca2+-permeable (ICa); Calcineurin-B Like Proteins (CBLs) proteins; CBL Interacting Protein Kinases (CIPKs), transcriptional factors; HSFs, heat shock transcription factors; Zats, zinc finger proteins; WRKYs, WRKY transcription factors; NPR1, nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related genes 1 (modified after Song et al. [18]).