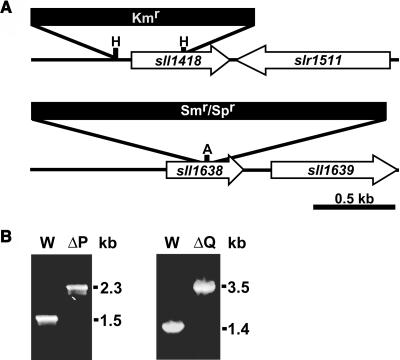
Figure 3.
Inactivation of the psbP and psbQ Genes in Synechocystis 6803.
(A) Restriction maps of the constructs for creating ΔpsbP (sll1418, top) and ΔpsbQ (sll1638, bottom) mutants. Restriction sites used are HincII (H) and AvaI (A). White arrows indicate the coding region for the disrupted gene and its closest neighboring open reading frame. Antibiotic resistance cassettes are for kanamycin (Kmr) and spectinomycin (Smr/Spr).
(B) PCR segregation analysis of the ΔpsbP (left panel) and ΔpsbQ (right panel) mutants. Genomic DNA from wild-type (W), ΔpsbP (ΔP), or ΔpsbQ (ΔQ) strains was the template for amplification with gene-specific primers to confirm segregation of the respective mutations.