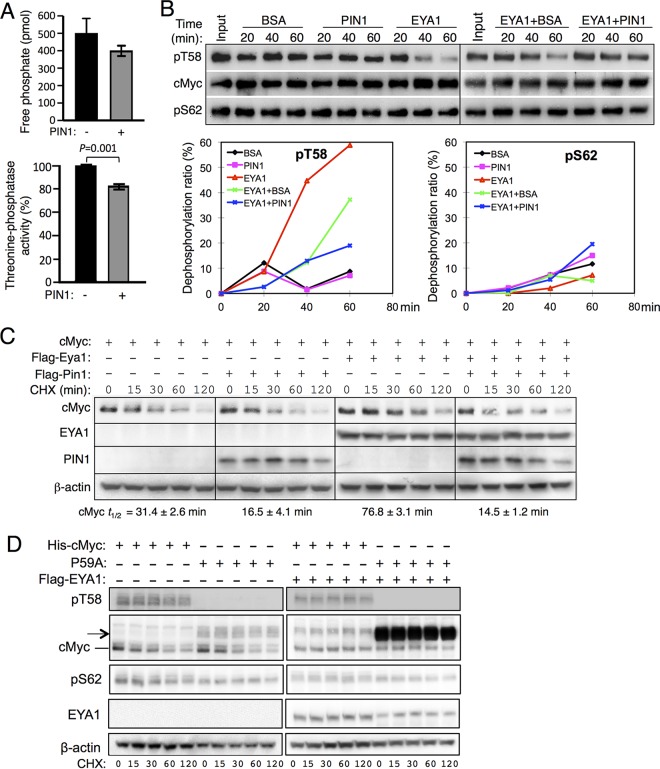
FIG 6.
Effect of PIN1 on EYA1-mediated dephosphorylation of Myc. (A) (Top) In vitro phosphatase assay of pT58-Myc wild-type peptide in the absence or presence of PIN1. (Bottom) Quantification of EYA1's threonine phosphatase activity and comparison between EYA1 alone and EYA1 together with PIN1. Addition of PIN1 reduced EYA1 activity to 83.1% ± 1.84% of its activity without PIN1. The experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated three times, and the data were reproducible. The error bars represent SD; the P value (<0.001) was calculated using StatView t tests. (B) PIN1 decreases EYA1-mediated Myc dephosphorylation. (Top) EYA1 dephosphorylates Myc at T58. Either BSA or PIN1 was added in the absence or presence of EYA1. (Bottom) Relative dephosphorylation ratios of pT58 (left) and pS62 (right) according to the quantification of Western blot data. (C) Western blot analysis. His-cMyc alone or together with Flag-Pin1 was transfected into 293 cells or Flag-Eya1-transfected stable 293 cells, and 40 h posttransfection, the cells were treated with cycloheximide (CHX) for different times before harvest. t1/2, half-life of cMyc. (D) Western blot analysis. His-cMyc or the His-P59A mutant was transfected into 293 cells or Flag-Eya1-overexpressing stable 293 cells cells, and 40 h posttransfection, the cells were treated with CHX for different times before harvest. t1/2, half-life of cMyc. Anti-pT58 failed to detect the phosphorylated-T58-P59A mutant protein. The arrow indicates the cMyc products with higher molecular weights in the P59A-transfected cells.