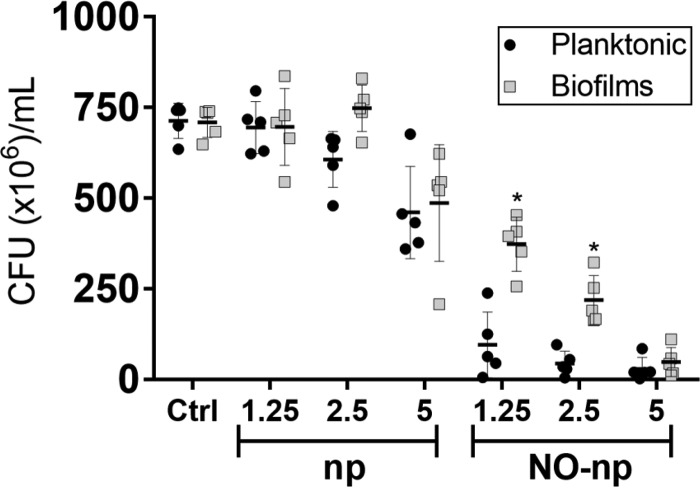
FIG 2.
NO-np are effective against S. aureus planktonic and biofilm-associated cells. The levels of bacterial viability of six distinct S. aureus clinical isolates in biofilms and planktonic cells were determined by CFU counts. Both phenotypes were exposed to 1.25, 2.5, and 5 mg/ml of np or NO-np for 24 h, and their viability was compared to that of bacteria (5 × 106 bacteria per ml) incubated in medium alone. For biofilm formation, the initial inoculum was 106 staphylococci per well. The biofilms were allowed to form for 24 h. Each symbol represents the result for a single strain. Black lines are the averages of the results for the six isolates, and error bars denote SDs. Statistical significance (*, P < 0.05 in comparing the results for biofilms and planktonic cells) was calculated by multiple t tests and adjusted by using the Holm-Sidak method. This experiment was performed twice, with similar results obtained each time.