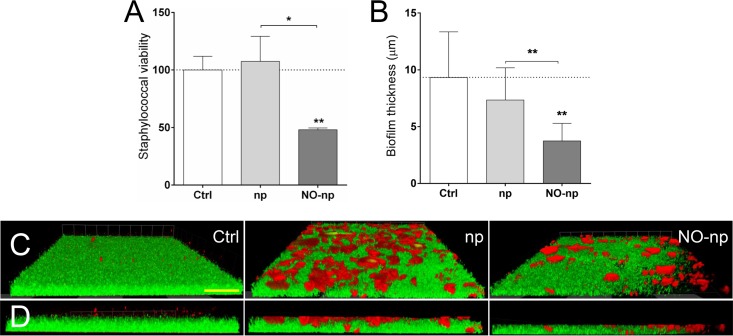
FIG 4.
MRSA 6498 cells within mature biofilms are effectively killed by NO-np. Microbial biofilms were grown on polystyrene microtiter or glass-bottom plates for 24 h at 37°C and incubated in the absence and presence of np or NO-np. For biofilm formation, the initial inoculum was 106 MRSA cells per plate. (A) The viability (percentage of control) of biofilm-associated cells was evaluated using the FDA assay. (B) The differences in biofilm thicknesses were examined after exposure to np or NO-np and compared with the biofilm thickness of the untreated control. (A and B) Bars represent the average results from three wells, and error bars denote SDs. Statistical significance (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01) was calculated by ANOVA. (C) Confocal microscopy of MRSA 6498 strain biofilms after treatment with NO-np. Images of mature bacterial biofilms showed exopolymeric matrix (red; stained with concanavalin A-Texas Red conjugate) and bacterial cells (green; stained with SYTO9). Images were obtained after 24-h coincubation of the bacterial cells in the absence and presence of np or NO-np. (D) The thickness and morphology of each biofilm can be observed in the Z-stack reconstruction. The pictures were taken at a magnification of ×100. (C and D) Scale bar represents 20 μm for all images. (A to D) These experiments were performed twice, with similar results obtained each time.