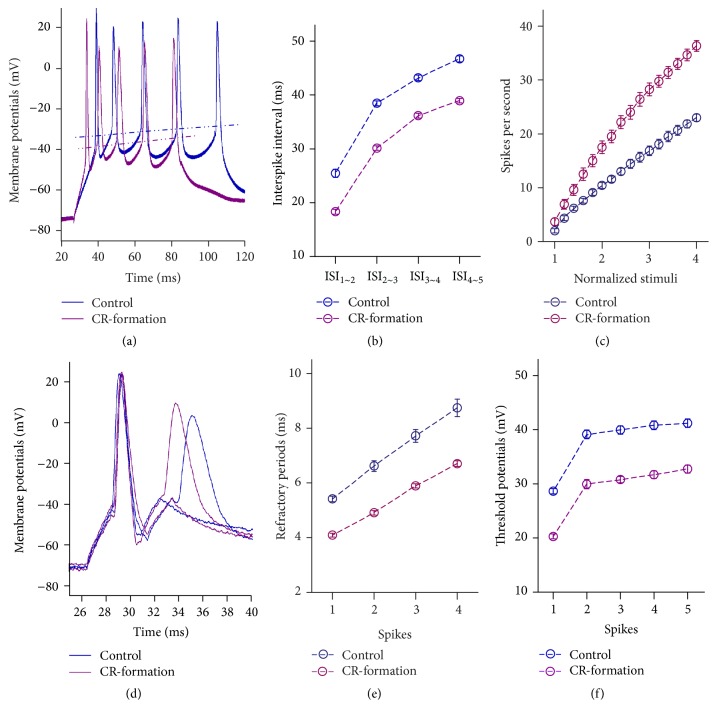
Figure 4.
The capability to encode spikes on barrel cortical pyramidal neurons increases after pairing WS and OS. The spikes were induced by depolarization pulse under voltage-clamp recording on glutamatergic neurons in cortical slices. (a) Traces illustrate depolarization-induced spikes on the neurons from control (blue trace) and CR-formation (dark-red). (b) shows interspike intervals for spikes 1~2 to spikes 4~5 from controls (dark-blue symbols, n = 21) and CR-formations (dark-red symbols, n = 20). (c) shows spikes per second versus normalized stimuli from control (dark-blue symbols, n = 21) and CR-formation (dark-red symbols, n = 20). (d) Traces show the measurements of spike refractory periods on the neurons from controls (dark-blue trace) and CR-formations (dark-red). (e) shows refractory periods versus spikes 1 to 4 from controls (dark-blue symbols, n = 21) and CR-formations (dark-red symbols, n = 20). (f) shows the threshold potential versus spikes 1 to 5 from controls (dark-blue symbols, n = 21) and CR-formations (dark-red symbols, n = 20).