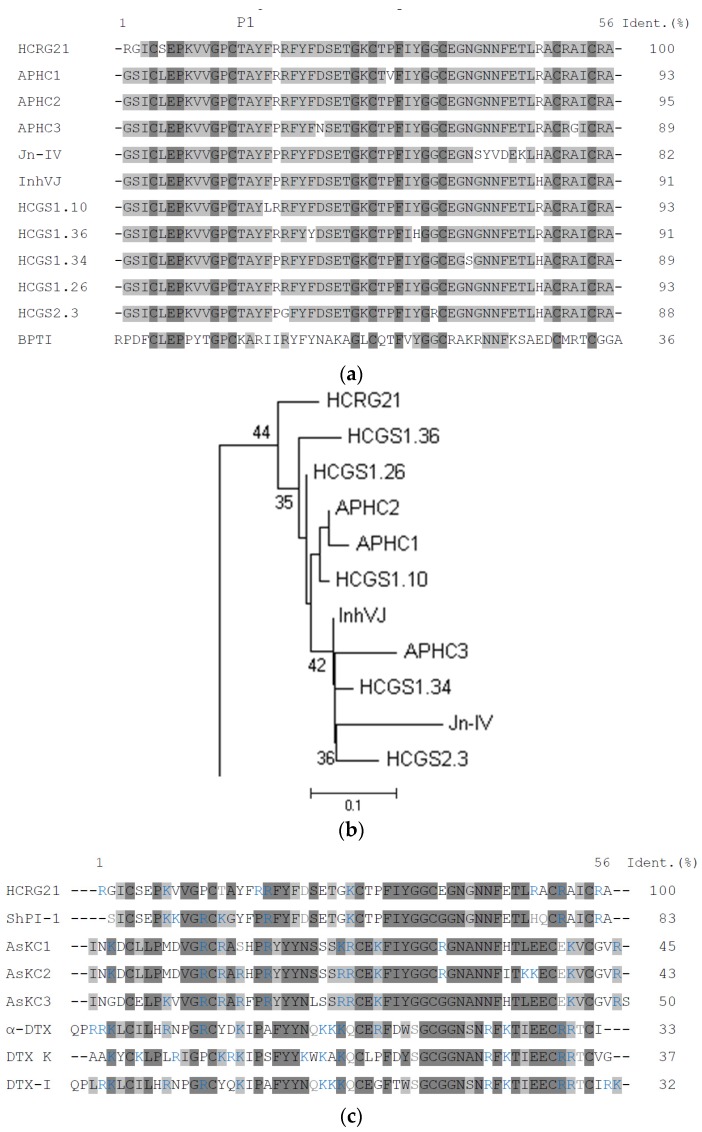
Figure 1.
(a) Alignment of H. crispa Kunitz-type peptides amino acid sequences. Analgesic peptides, APHC1, APHC2, APHC3 [28,29], Jn-IV [14], InhVJ [16], and representatives of HCGS peptide family with P1Thr from the combinatorial library, obtained from H. crispa cDNA [11]: HCGS1.10, HCGS1.36, HCGS1.34, HCGS1.26, and HCGS2.3; and BPTI from bovine pancreas [55]. P1—amino acid residue of the inhibitor reactive center. Identical and conservative residues are indicated by dark and light gray colors. The asterisks below the sequence of BPTI indicate the contact sites with serine proteases; (b) Evolutionary relationships of H. crispa sea anemone Kunitz-type peptides. The NJ phylogenetic tree was made using the Poisson correction with bootstrap test of 1000 replications in MEGA 6 [56]. Nodes with confidence values greater than 30% are indicated; (c) Comparison of amino acid sequences of H. crispa HCRG21, ShPI-1 from S. helianthus [22], AsKC1–AsKC3 from A. sulcata [7] and α-DTX, DTX-K, and DTX-I from the snake Dendroaspis polylepis [53]. Identical and conservative residues are indicated by dark and light gray colors, respectively. Positive charged residues are colored in blue.