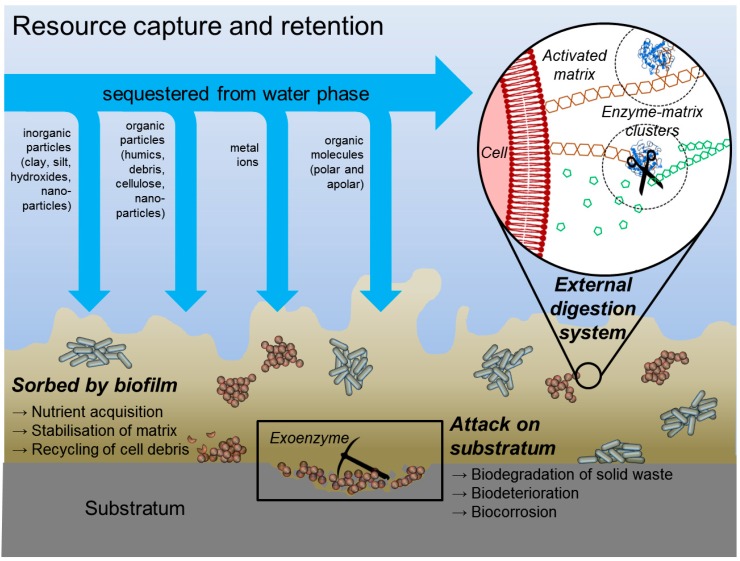
Figure 2.
Resource caption and retention by and in biofilms. The biofilm is a sponge-like system that provides surfaces for the sorption of a diverse range of molecules that can be sequestered from the environment. This confers several benefits to the biofilm, such as nutrient acquisition and matrix stabilization. Similarly, the physicochemical properties of the matrix enable biofilms to retain and stabilize extracellular digestive enzymes produced by biofilm cells, turning the matrix into an external digestive system. Surface-attached biofilms are not only able to take up nutrients from the water phase but can also digest biodegradable components from the substratum, which is exposed to enzymes in the matrix (after [19], with permission).